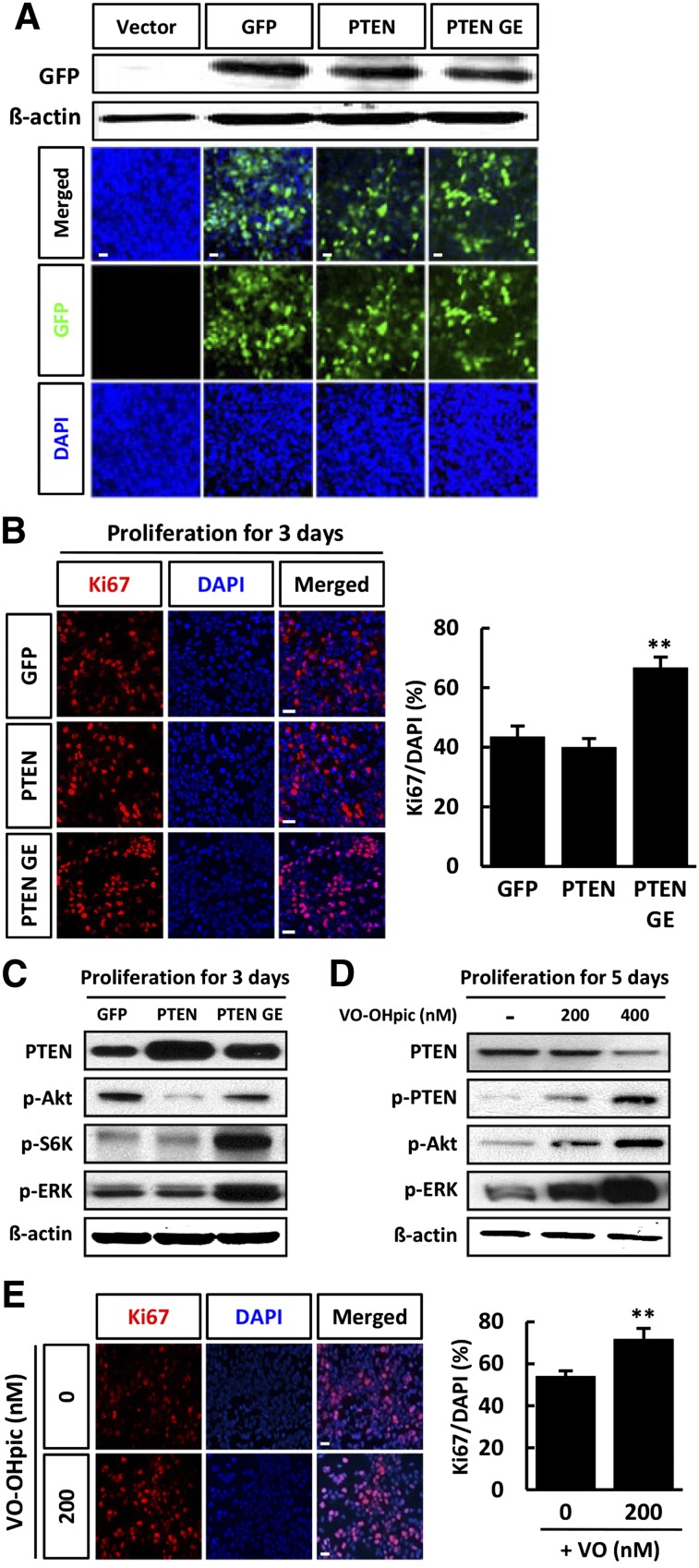
Figure 4.
PTEN inhibition promoted the proliferation of human neural stem cells (hNSCs). (A): hNSC cultures were infected in parallel with vectors expressing PTEN-GFP, PTEN G129E-GFP, or GFP and cell lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with antibody against GFP. (B): Infected cells were cultured for 3 days in conditions of proliferation. Representative immunofluorescence for Ki67 (red) and fluorescent staining of DAPI (blue), and the proportion of Ki67-positive cells were calculated. (C): Lysates of proliferative cells were subjected to immunoblotting for PTEN, p-Akt, p-S6K, p-ERK, and β-actin, as indicated. Each blot represents three independent experiments. Chemical inhibition of PTEN increases proliferation of hNSCs. hNSCs were treated with or without VO-OHpic during proliferation (in the presence of basic fibroblast growth factor) (D, E). (D): hNSCs were cultured under conditions of proliferation in the presence or absence of VO-OHpic (200 or 400 nM) for 5 days, and lysates were subjected to immunoblotting with PTEN, p-PTEN, p-Akt, p-ERK, and β-actin, as indicated. Each blot represents three independent experiments. (E): Representative immunofluorescence for Ki67 (red) and fluorescent staining of DAPI (blue) are shown, and the proportion of Ki67-positive cells was calculated. Error bars are standard errors of the mean (SE). ∗∗, p < .001 in comparison with control cells. Scale bar = 20 μm. Abbreviations: DAPI, 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; GE, PTN-G129E-GFP (a catalytically inactive PTEN mutant); GFP, green fluorescent protein; p, phosphorylated; PTEN, phosphatase and tension homolog; PTEN GE, a catalytically inactive PTEN mutant; S6K, S6 kinase.