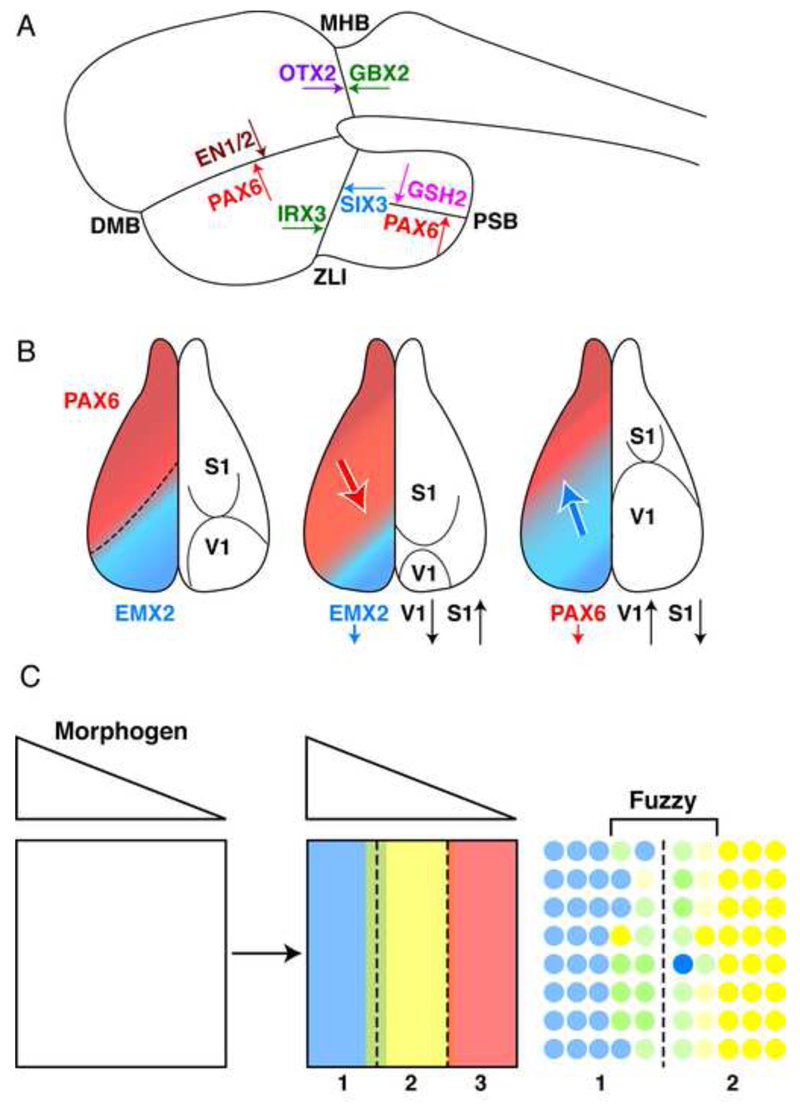
Figure 1.
Homeoproteins and boundary formation. A. Examples of boundaries defined by the expression of abutting homeoproteins with self-activating and reciprocal inhibitory properties. B. The classical example of the competitive activities of Emx2 and Pax6 in the definition of primary somato-sensory and visual cortex areas in the developing mouse cortex. The latter work by the group of Denis O’Leary (O’Leary et al., 2007) refers to the cell autonomous activity of homeoproteins and does not consider their non-cell autonomous activity. C. The graded expression of a morphogen creates several domains within the morphogenetic field, according to the Wolpert’s French flag paradigm (Wolpert, 1969). Each domain is characterized by the expression of a homeoprotein transcription factor (Blue-Yellow-Red) but the boundaries are initially fuzzy.