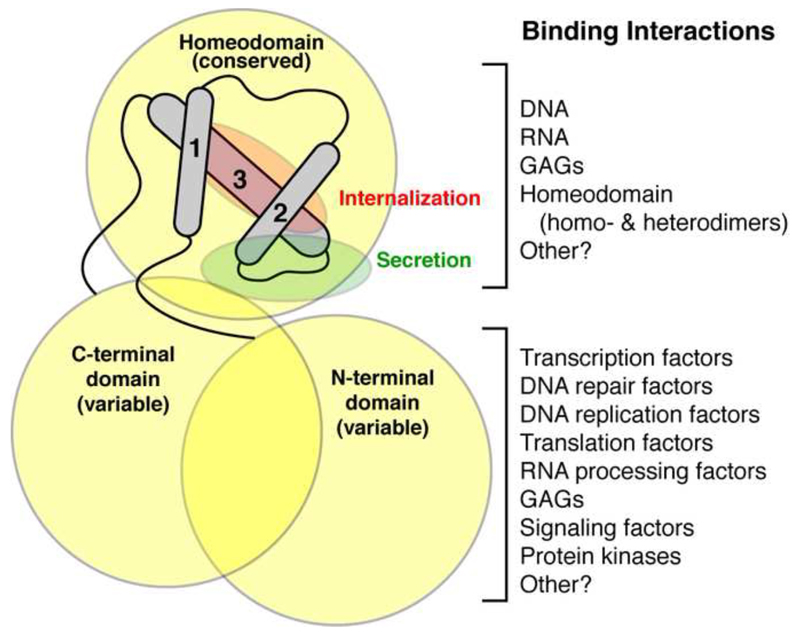
Figure 3.
Homeoproteins bind to a wide range of molecules. The homeodomain contains a conserved 3-helix bundle flanked by variable N- and C-terminal domains that together form the homeoprotein. These domains make a plethora of interactions with DNA, RNA, GAGs and proteins. Consequently, homeoproteins are shown to regulate transcription, RNA processing and translation, DNA replication and damage response and are also implicated in cell signaling. Within the 2nd and 3rd DNA-binding α-helices are the motifs that permit the non-conventional secretion and internalization of the homeodomain.