Figure 1. Neuroglial interactions in the rostral ventrolateral medulla oblongata hypothesized to underlie pathological increases in sympathetic nerve activity in chronic heart failure and essential hypertension .
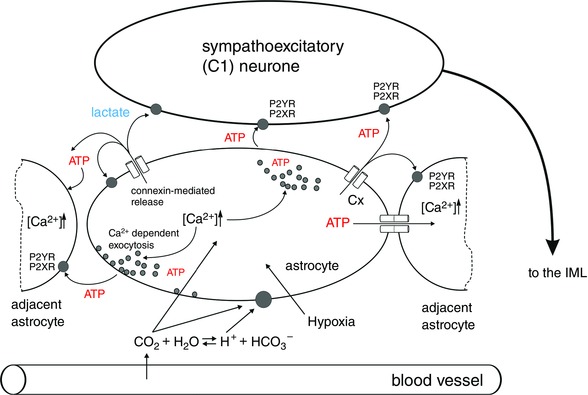
Tissue hypoxia and increased concentration of CO2/H+ is detected by astrocytes, leading to the release of ATP and lactate, which in turn increase the excitability of bulbospinal sympathoexcitatory (C1) neurones. Abbreviations: Cx, connexin; and IML, intermediolateral cell column.
