Fig. 2.
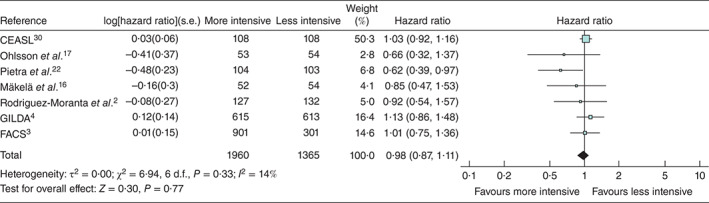
Forest plot showing hazard ratios for death in seven randomized comparisons of more and less intensive follow-up from which hazard ratios could be derived. An inverse-variance random-effects model was used to produce an overall estimated hazards ratio. Hazard ratios are shown with 95 per cent confidence intervals. The studies are ordered according to the year of the start of the inclusion. CEASL is dominant because the weight of the study is dependent on the follow-up time, number of events and number of patients in each treatment arm. The Kaplan–Meier curve in CEASL is plotted up to 25 years. The point estimate in favour of more intensive monitoring in studies by Rodriguez-Moranta et al.2 and Pietra and colleagues22 was attributed by the authors to detection by endoscopy and successful treatment of recurrent rectal carcinoma
