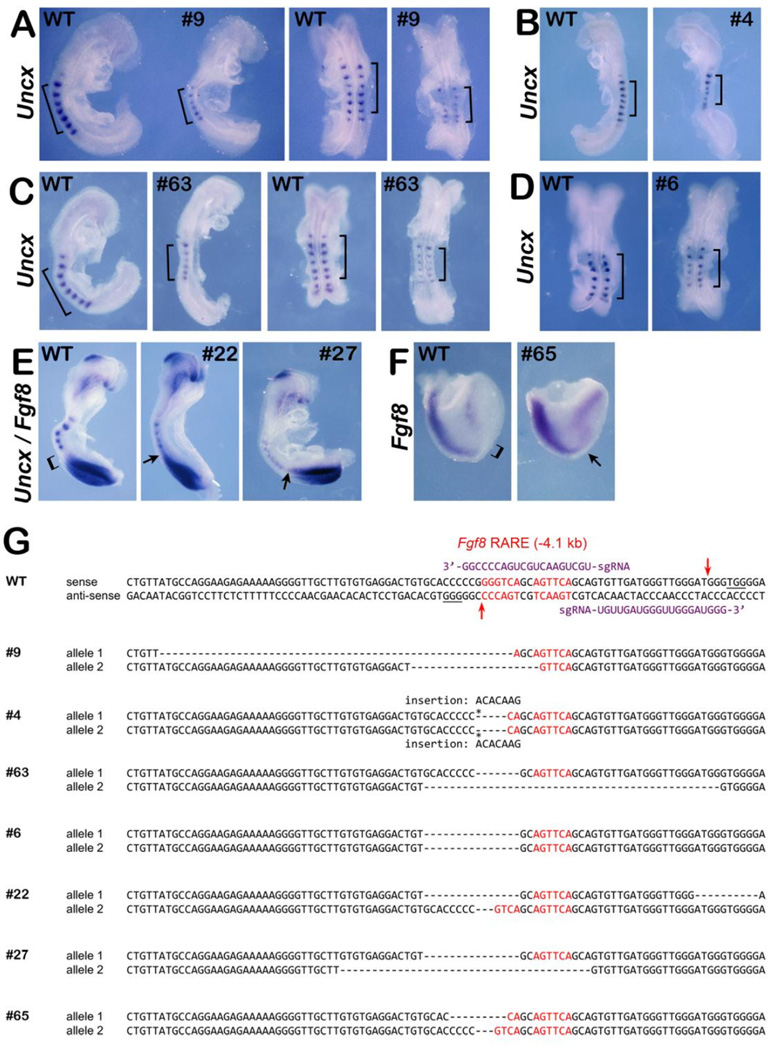
Fig. 5.
Deletion of Fgf8 RARE in mouse embryos results in small somite phenotype and ectopic caudal Fgf8 expression. Shown are the results obtained from mutant embryos generated by CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing near the Fgf8 RARE. (A–D) Wild-type (WT) and mutant embryos with the same number of somites (or differing by 1 somite) analyzed for Uncx mRNA (a somite marker); brackets mark 6-somite regions for each embryo. (E) Embryos analyzed for expression of both Fgf8 and Uncx and (F) embryo analyzed for expression of only Fgf8; brackets indicate regions normally devoid of Fgf8 expression in WT whereas arrows point out regions of ectopic Fgf8 expression in mutants. (G) dsDNA sequence of wild-type Fgf8 RARE region (Kumar and Duester, 2014); sequence in red indicates the two 6 bp half sites of the Fgf8 RARE; PAM sequences are underlined; sgRNA guide sequences and their respective binding positions are shown in purple; arrows represent targeted Cas9 cleavage sites. Also, shown are the DNA sequences of CRISPR/Cas9-generated mutants (sense strand of both alleles shown); sequences in red indicate the Fgf8 RARE half-sites; dashes indicate deletions and asterisks indicate insertions.