Figure 4.
Co-occurrence of H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 Scales with Expression
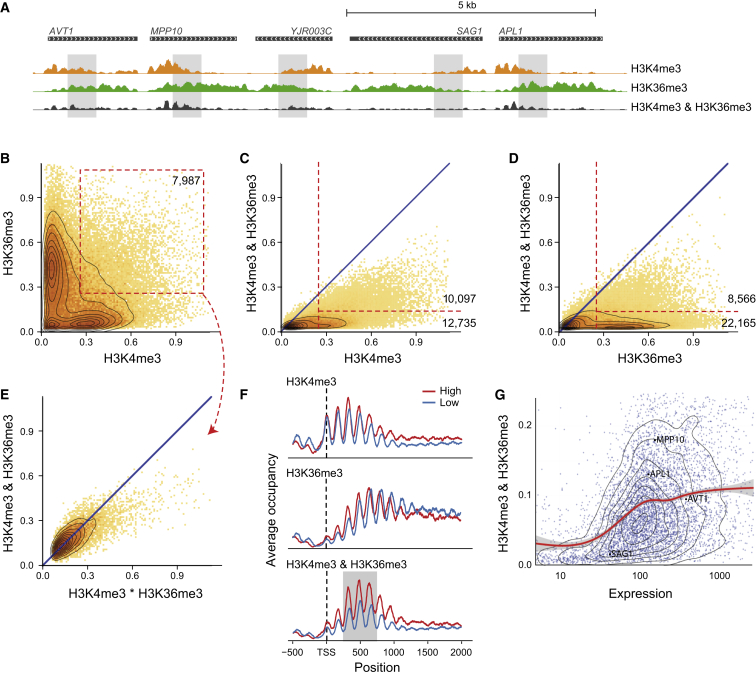
(A) Polymerase-deposited marks H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 appear at gene start and body, respectively. Shown is a representative genomic region. Overlapping regions of the individual signals show combinatorial-iChIP signal (gray area).
(B) Scatter of normalized H3K4me3 and H3K36me3 individual ChIP levels on all nucleosomes. Most nucleosomes have strong signal for one or the other marks. A subpopulation of nucleosomes show co-enrichment for both marks (red box).
(C and D) Comparison of individual ChIP to combinatorial-iChIP (as in Figures 3B and 3C). Red lines denote population of nucleosomes with high levels of the individual ChIP signal and either low or high levels of combinatorial-iChIP signal.
(E) Comparison of expected co-occurrence signal by chance versus combinatorial-iChIP signal (as in Figure 3E) for the subpopulation marked in (B).
(F) Meta genes of ChIP signal of H3K4me3, H3K36me3, and their combinatorial-iChIP. “High” and “low” denote averages on genes in the 80%–100% and the 20%–40% quantiles of expression, respectively. Combinatorial-iChIP signal is highest in nucleosomes +3 to +5 (gray background).
(G) Comparison of expression levels of genes to the average combinatorial-iChIP signal on nucleosomes +3 to +5 (area marked in gray in F). Red line marks the smoothed mean (gray area, confidence interval in the mean). The location of genes shown in (A) are marked on the scatterplot.