Figure 1.
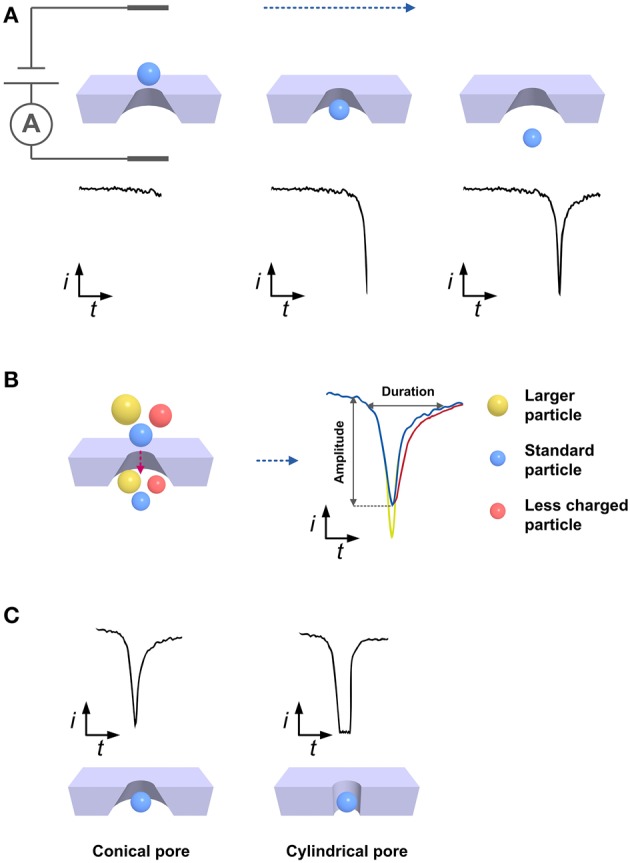
Schematic illustrating basic principles of nanopore-based RPS technique. (A) Current changes during particle translocation across the nanopore. (B) Differences in pulses resulting from the translocation of particles with different sizes or surface charges. The yellow sphere is larger than the blue one and they carry the same amount of surface charge. The red sphere is less charged compared to the blue one and they have the same size. (C) Effect of pore's geometry on pulse shape. Conical and cylindrical pores commonly give rise to the asymmetric and symmetric pulses.
