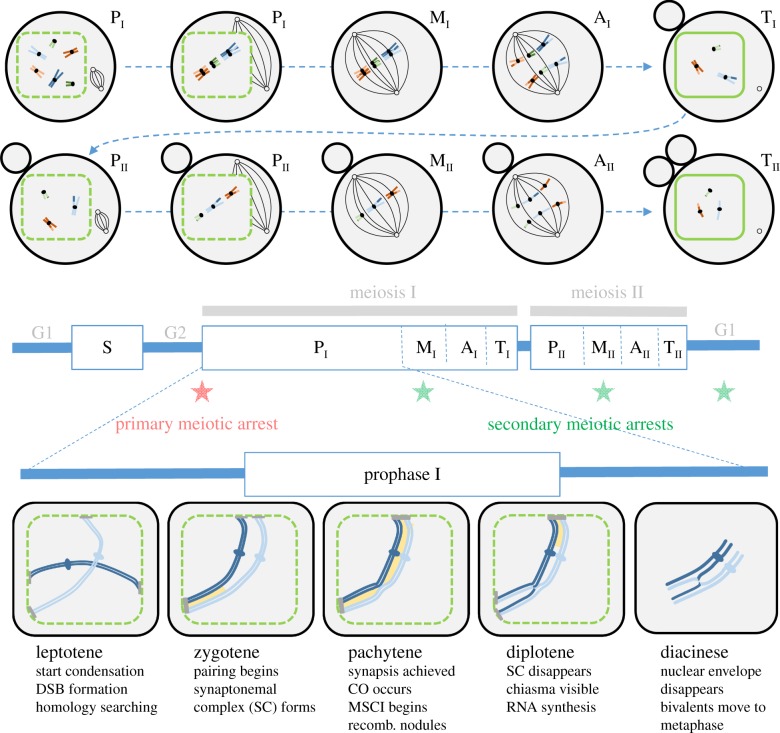
Figure 1.
Schematic of the different steps in standard meiosis. The top panel illustrates the different phases of a typical female meiosis for each of the two meiotic divisions: prophase (P, with early and late prophase distinguished), metaphase (M), anaphase (A) and telophase (T). The nuclear membrane is indicated by the green contour (dashed when it starts fragmenting). The small black circles represent microtubule organizing centres and the black lines represent microtubules of the meiotic spindle. First and second polar bodies are shown as grey circles next to the oocyte (chromosomes inside the polar bodies are not shown). Homologous chromosomes are represented with the same colour with slightly different shades (e.g. orange and light orange). Homologues pair and segregate in meiosis I, then sister chromatids segregate in meiosis II. The middle panel shows the meiotic cell cycle. The timing of the primary meiotic arrest is indicated by a red star, while the timing of the most common secondary arrests in different organisms is indicated by green stars (see §4a). The lower panel indicates the important steps (DSB formation, crossing overs) occurring during prophase I. The synaptonemal complex is shown in yellow. Chromatin condenses in chromosomes throughout prophase I (only one pair of homologues is illustrated). In most species, telomeres attach to the nuclear envelope. The attachment plate is indicated by a grey bar. MSCI, meiotic sex chromosome inactivation (see §4d).