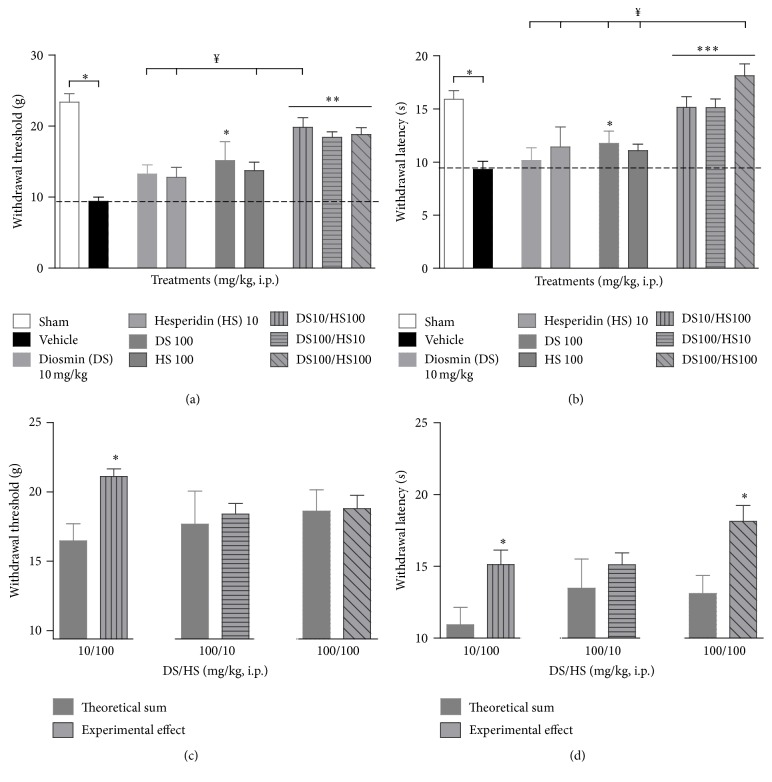
Figure 3.
Effects of acute treatment of single hesperidin (HS, 10 and 100 mg/kg) and diosmin (DS, 10 and 100 mg/kg) in comparison with their combinations (DS10/HS100, DS100/HS10, and DS100/HS100 mg/kg) on the mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia after CCI surgery in rats. Column graphs show the effect of hesperidin, diosmin, these flavonoid combinations, and control groups (sham and vehicle) on the withdrawal threshold after mechanical stimulus (a) and on the withdrawal latency after thermal stimulus (b). To analyze the effect of the combinations, the antihyperalgesic response of each one in mechanical (c) and thermal (d) stimuli was contrasted with its respective theoretical antihyperalgesic value (represented from the maximal response obtained in the vehicle group, - - -, (a-b)) and also compared to the effect obtained experimentally (c-d). Each column is the average value of the withdrawal threshold or withdrawal latency ± SEM in at least six rats. For panels (a) and (b), one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's test, symbols indicate statistical significance, ∗∗ P < 0.01 and ∗∗∗ P < 0.001 versus vehicle, whereas ¥ P < 0.001 for comparison among combinations versus individual treatment. For panels (c) and (d), Student's t-test, ∗ P < 0.01.