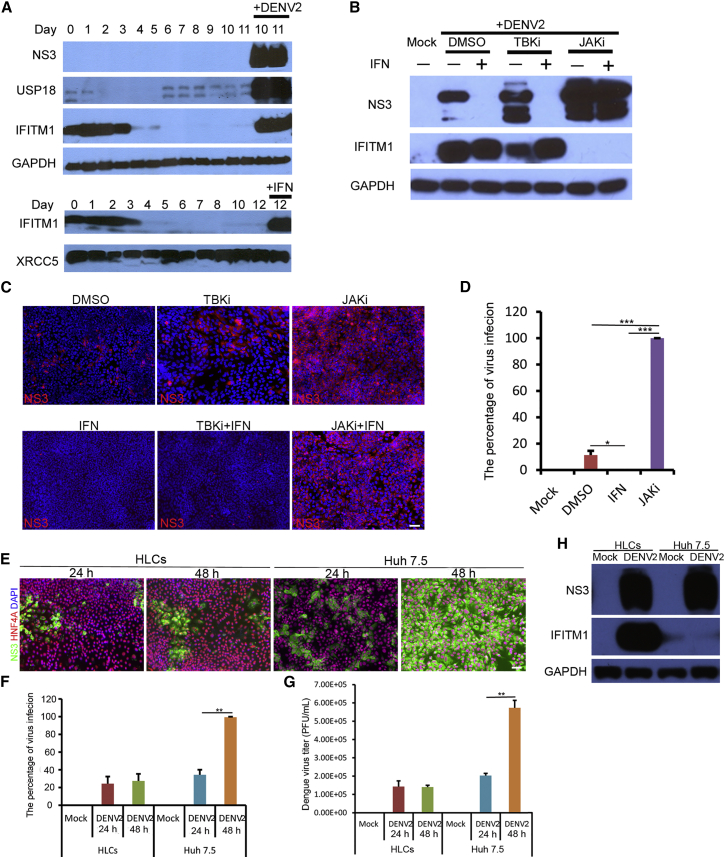
Figure 3.
Interferon Response Induced by DENV Infection in HLCs
(A) Upregulation of IFITM1 and USP18 upon DENV2 infection. The hESCs (day 0) and differentiated cells from day 1 to day 11 were inoculated with or without DENV2, and cell lysates were collected 48 hr post infection for western blotting. IFN-α2a-treated cells at day 12 were used as a positive control.
(B) Inhibition of IFN signaling pathway enhanced DENV2 infection. HLCs at day 15 were pretreated with DMSO (0.1%), JAK inhibitor (1 μM), or TBK1 inhibitor (2 μM) for 3 hr, followed by incubation with or without IFN-α2a (1,000 U/mL) for 8 hr. Cells were then infected with DENV2 at an MOI of 0.3 for 48 hr. Cell lysates were collected for western blotting.
(C) Inhibition of IFN signaling resulted in the spread of DENV2. Cells were treated as described above, and infected by DENV2 at an MOI of 0.01 for 72 hr. Cells were fixed and stained for immunostaining. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(D) Statistical analysis of the percentage of DENV infection. HLCs were pretreated with DMSO, JAKi, and IFN as described above, then infected by DENV2 at an MOI of 0.5 for 48 hr. The percentage of DENV infection in each sample was analyzed by immunostaining assay.
(E–G) Comparison of virus infection between HLCs and Huh 7.5 cells. Both HLCs and Huh 7.5 cells were infected by DENV2 at an MOI of 1 for 48 hr. Cell samples and the supernatants were collected every 24 hr for immunostaining analysis (E), infection rate calculation (F), and virus titration (G). Cells were washed stringently before medium change. Scale bar, 50 μm.
(H) No induction of IFITM1 in Huh 7.5 cells upon DENV2 infection. Cells were treated as described above. Cell samples were collected at 24 hr post infection for western blotting.
Three independent experiments were performed. Data are presented as mean ± SD. p Values were calculated by Student's t test: ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S3.