Figure 4.
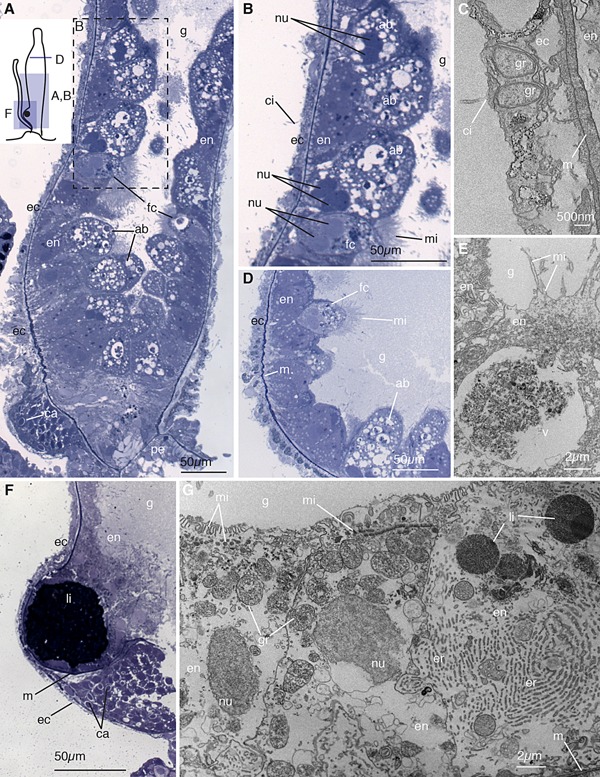
Palpon. (A) Longitudinal thick section of the base of the palpon. Schematic in the top left shows the orientation of panels (A), (B), (D), and (F). Visible are funnel cells (fc) and absorptive cells (ab) in the endoderm (en) lining the gastric cavity (g), the ectoderm (ec) including the reduced basigaster region with forming capsules (ca), and the peduncle (pe) that connects to the stem. (B) Enlarged image of region boxed in (A) showing the absorptive and funnel cells with microvilli (mi). Pairs of nuclei (nu) within a single cell are visible. Ectodermal cilia (ci) are also visible. (C) Longitudinal electron micrograph of the ectoderm showing cilia and beta granules (gr), and mesoglea (m). (D) Transverse thick section of the mid‐region of the palpon, showing funnel cells endodermally and thin ectoderm. (E) Longitudinal electron micrograph of the endoderm, showing funnel cells with microvilli arranged in clusters at the apex, and containing a large vacuole (v). (F) Longitudinal thick section of the base of the palpon, showing the mesoglea (m) partially surrounding a lipid droplet (li). A reduced basigaster can be observed basal to the droplet. (G) Longitudinal electron micrograph of endoderm cells from surface to mesoglea, showing rows of microvilli, a well developed endoplasmic reticulum (er), beta granules, and lipid droplets. Panels (A), (B), (D), and (F) are thick sections (0.5–0.75 μm) stained with toluidine blue, and panels (C), (E), and (G) are electron micrographs (90 nm).
