Figure 1.
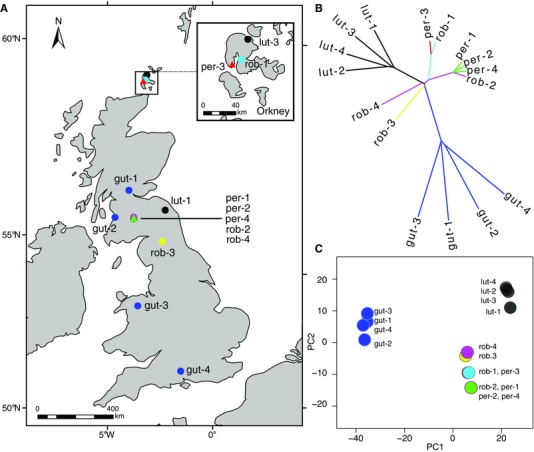
Geographic location and genomic relationships between 16 individuals of Mimulus spp. in each of four taxa: M. guttatus (gut), M. luteus (lut), M. x robertsii (rob), and M. peregrinus (per). (A) Map of the United Kingdom showing the geographic location of the samples analyzed here. Two individuals of M. luteus (lut‐2 and lut‐4) were collected in Chile and are not shown in this map. (B) Neighbor joining tree showing monophyletic clades for the parental taxa (M. guttatus and M. luteus), and clustering of the allopolyploid M. peregrinus with geographically proximate populations of M. x robertsii. Bootstrap support for all nodes is shown in Figure S3. (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) plot showing clustering of individuals along the first two principle components. Mimulus peregrinus and M. robertsii fall between parental species, M. guttatus and M. luteus and next to geographically proximate M. x robertsii.
