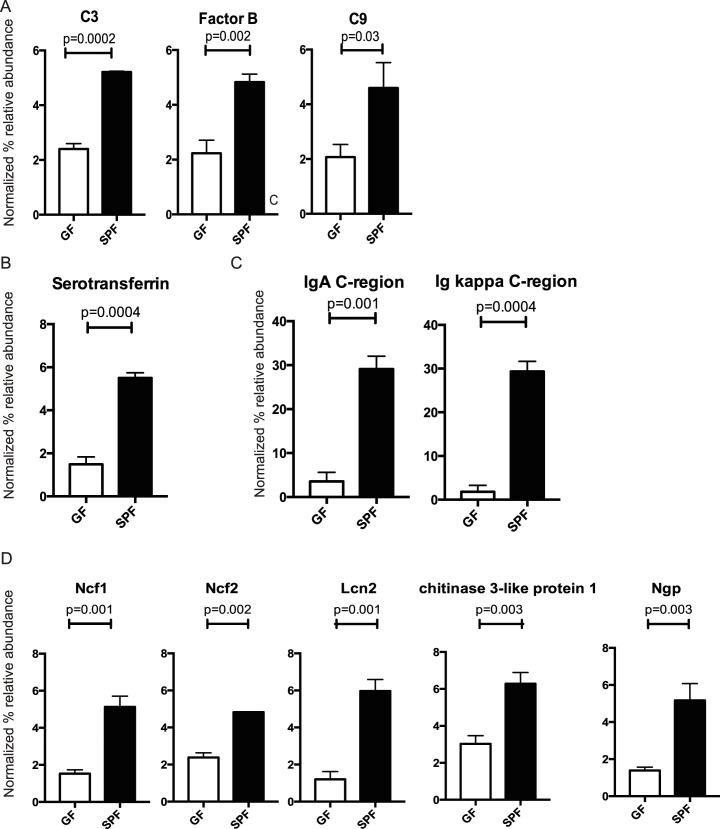
Fig 1. GF mice have decreased levels of innate and adaptive immune effectors at the ocular surface.
A. Significantly decreased levels of complement proteins at the ocular surface in GF mice compared to SPF mice. B. Significantly decreased levels of iron binding protein serotransferrin at the ocular surface. C. Decreased levels of immunoglobulins at the ocular surface. D. Decreased levels of neutrophil-derived peptides at the ocular surface. Significant differences were detected in the levels of nuclear cytosolic protein 1 (Ncf1) and 2 (Ncf 2), myeloid bactenecin (ngp), neutrophil galatinase associated lipocalin (Lcn2), and chitinase-3-like protein 1. Ocular surface washes were pooled from GF (n = 5) and SPF mice (n = 5). Two-three biological replicates were analyzed per experiment. Five μg total protein were digested with trypsin, peptides were labeled, multiplexed with TMT, and quantified using LC-MS3. p-values were calculated using Benjamini-Hochberg FDR correction.