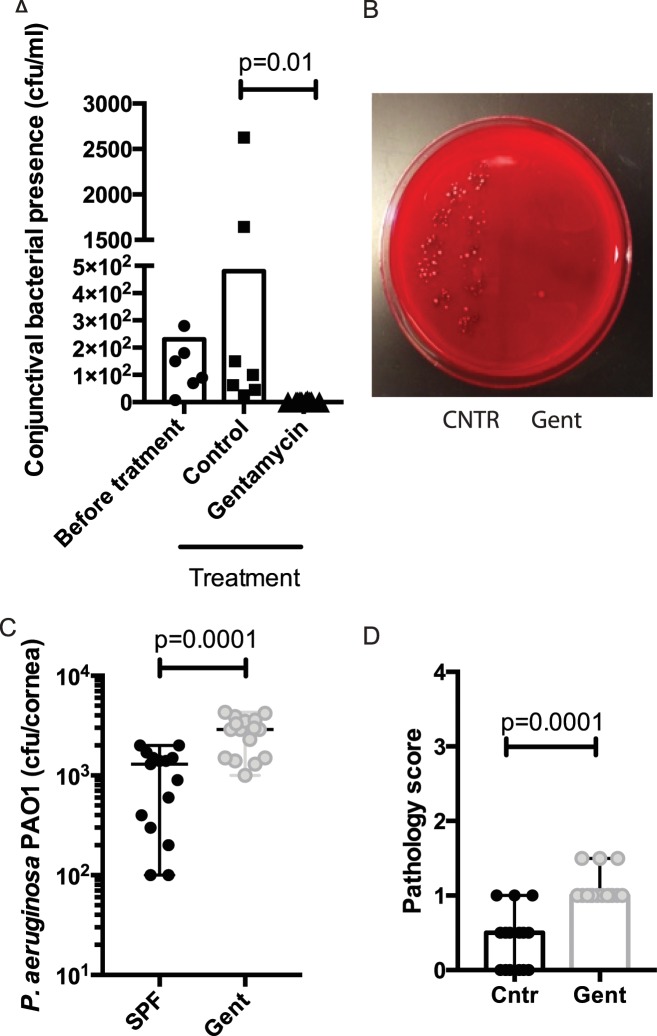
Fig 5. Topical gentamycin treatment reduces the resistance to P. aeruginosa-induced keratitis.
A. Commensal conjunctival presence in SPF mice (n = 10) is significantly higher than in mice (n = 10) treated topically with gentamycin ointment for 3 days prior to the infectious challenge. Data were pooled from two independent experiments. Groups were compared with one-way ANOVA, p = 0.01. B. Detection of bacterial growth from conjunctival swabs on a blood agar plate. The left side of the plate was seeded with 10 μl/spot suspension derived from the conjunctival swabs of control mice, the right side of the plate was seeded with 10 μl/spot suspension derived from the conjunctival swabs of Gentamycin-treated mice. C. Corneal bacterial burden after challenge with P. aeruginosa PAO1 is moderately but significantly increased in the Gentamycin–treated cohort. Data were pooled from three performed experiments. Unpaired Student’s t-test. D. Pathology scores. p-values are derived by Mann-Whitney test.