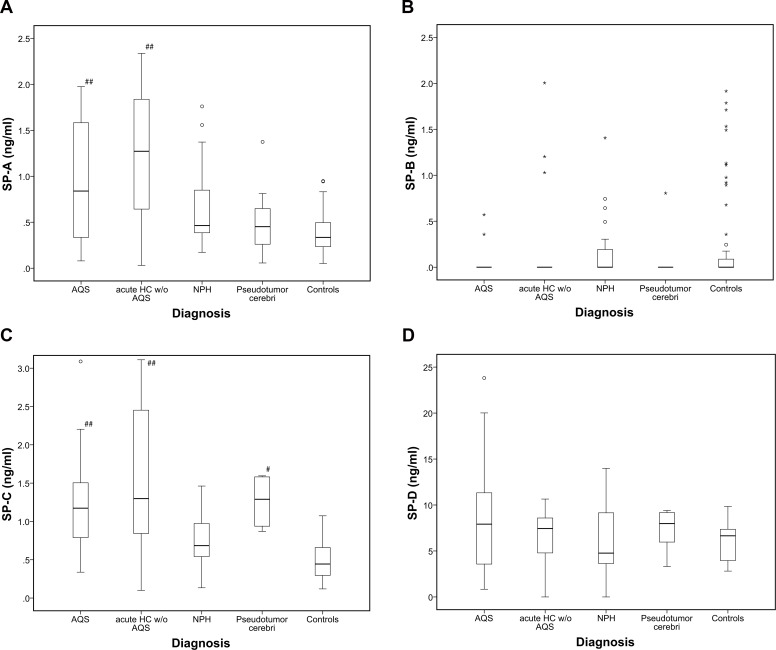
Fig 1.
a) CSF levels of SP-A (ng/ml) in control group and hydrocephalus subgroups. In acute hydrocephalic conditions with elevated intracranial pressure (ICP), SP-A levels are significantly elevated. b) CSF levels of SP-B (ng/ml) in control group and hydrocephalus subgroups. SP-B is not significantly altered in hydrocephalus groups compared to control. SP-B concentrations in most specimens were below the detection limit. Detectable SP-B values showed a wide range of variation. c) CSF levels of SP-C (ng/ml) in control group and hydrocephalus subgroups. Compared to controls, SP-C is significantly increased in subgroups with elevated ICP. d) CSF levels of SP-D (ng/ml) in control group and hydrocephalus subgroups. SP-D is present under normal and pathological conditions, there are no significant differences between the subgroups of AQS and controls. Significance levels: # p<0.05 ## p<0.001; all vs. Control. *: Data value lies >3 times of the interquartile range away from the mean value. °: Data value lies between 1.5 and 3x of the interquartile range away from the median value.