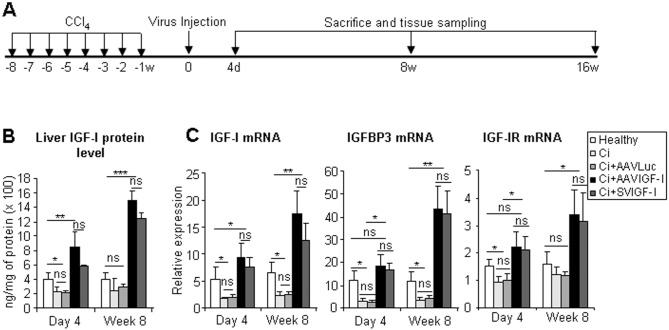
Fig 1. Functional IGF-I is expressed in the liver after administration of AAVIGF-I or SVIGF-I.
(a) Schematic of the experimental protocol used. Healthy animals were untreated, or used to induce liver cirrhosis by intragastric administration of CCl4 once a week for eight weeks (w). One week after the end of the cirrhosis induction protocol, cirrhotic animals were treated with saline, AAVLuc, AAVIGF-I or SVIGF-I by intra-arterial administration. Animals were sacrificed 4 days, 8 weeks and 16 weeks after vector inoculation. Healthy animals were sacrificed in parallel as controls. Blood was collected and liver samples were processed for histology, and purification of RNA and proteins for further analysis. (b) Analysis of liver IGF-I expression and activity. Liver samples were obtained from healthy, cirrhotic animals treated with saline (Ci), AAVLuc (Ci+AAVLuc), AAVIGF-I (Ci+AAVIGF-I) or SVIGF-I (Ci+SVIGF-I). Total IGF-I protein (a) and IGF-I, IGFBP3 and IGF-IR mRNAs were quantified by ELISA and qRT-PCR in liver extracts. Transcript levels shown are relative to glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) mRNA levels. Samples were obtained 4 days or 8 weeks after vector inoculation. Error bars denote standard deviations. Significant and non-significant (ns) differences are highlighted.