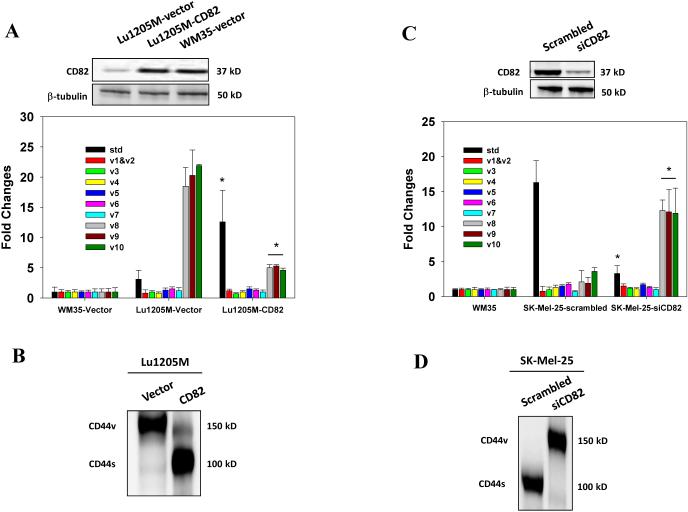
Figure 3.
Regulation of alternative splicing of CD44 pre-mRNA by CD82. (A) After transfection of WM35 or Lu1205M with a plasmid encoding CD82 or vector alone, amounts of CD44 standard and variable exons (v1-v10) in the central viable region were measured with real-time PCR. Values were expressed as fold changes (mean±SEM, n=3) relative to respective levels in WM35-vector cells. *p<0.05 compared with Lu1205M-vector. CD82 transfection efficiency was assessed by Western blotting. (B) The effect of CD82 overexpression on CD44 isoform switches in Lu1205M was measured by Western blotting. (C) The amounts of standard CD44 standard and variable exons (v1-v10) in SK-Mel-25 cells which received scrambled or CD82 siRNA were measured with quantitative real-time PCR. Values were expressed as fold changes (mean±SEM, n=3) relative to respective levels in WM35 cells. *p<0.05 compared with SK-Mel-25-siCD82. CD82 knockdown efficiency was assessed by Western blotting. (D) The effect of CD82 knockdown on CD44 isoform switches in SK-Mel-25 cells was measured by Western blotting. Representative results are shown from three independent experiments.