Fig. 5.
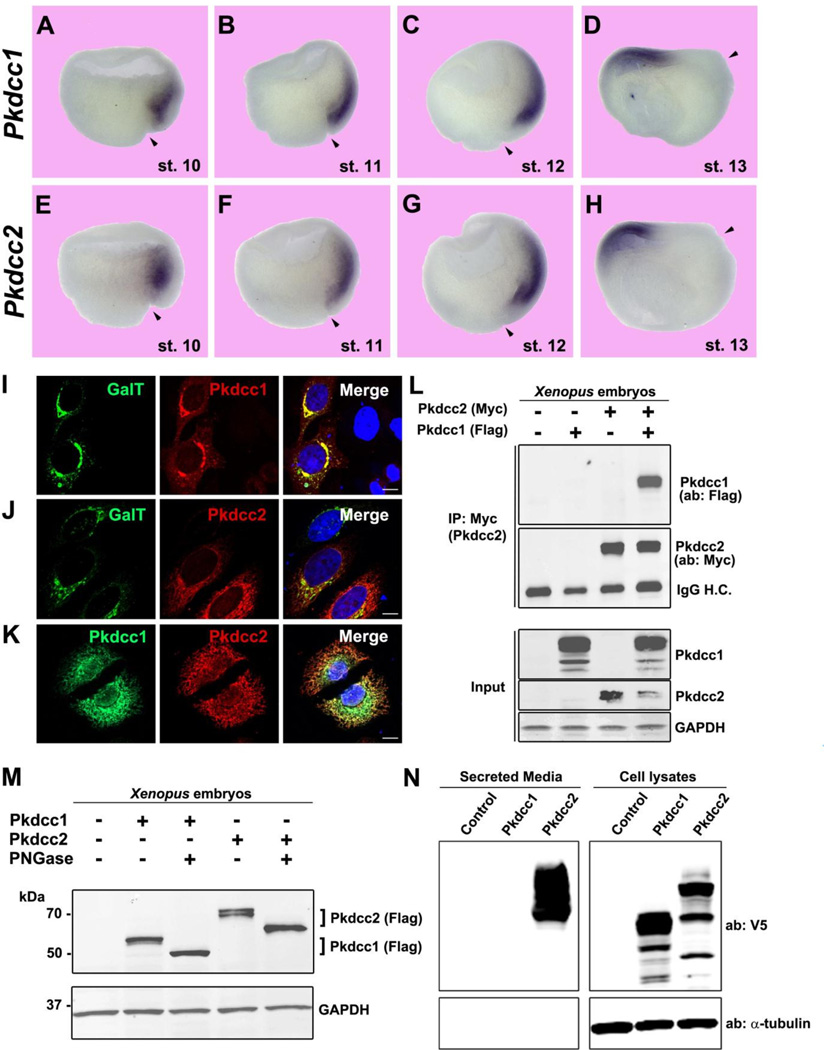
Pkdcc1 and 2 are expressed in the Spemann Organizer and localize to the Golgi apparatus. (A–H) Whole-mount in situ hybridization on hemisectioned Xenopus gastrula embryos showing Pkdcc1 and Pkdcc2 expression pattern from early to late gastrula (stage 10–13). Note the more anterior localization (in anterior endomesoderm) of Pkdcc2 compared to Pkdcc1 at stage 10. By the end of gastrulation Pkdcc1/2 expression was restricted to the prechordal plate. Arrowheads indicate dorsal lip position. (I–K) Immunofluorescence on HeLa cells overexpressing Pkdcc1-Flag and Pkdcc2-myc shows that the two kinases co-localize with the Golgi marker Galactosyl-Transferase (GalT). The two kinases also showed an overlapping subcellular localization. Nuclei were stained with DAPI (merge). Scale bars represent 10 µm. (L) Immunoprecipitation experiment showing physical interaction between Pkdcc1 and Pkdcc2 in Xenopus embryos. Pkdcc1-flag and/or Pkdcc2-myc mRNAs were injected at 4-cell stage and embryos were lysed at stage 12. One third of the total protein extract was saved and used as input. (M) Pkdcc1 and 2 are glycosylated, as shown by the electrophoretic mobility shift caused by PNGase F treatment. (N) Analysis of V5-tagged Pkdcc1 and 2 secretion in HEK293T cells showing that Pkdcc2 was found in the culture medium, indicating extensive secretion.