Figure 4.
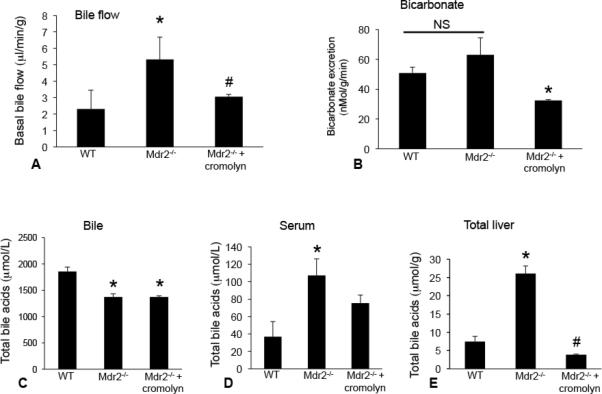
In vivo, we measured the effects of cromolyn sodium treatment on bile flow, bicarbonate excretion and total bile acid (TBA) concentration. In Mdr2−/− mice there was increased bile flow; however, treatment with cromolyn sodium significantly reduced bile flow (A). Bicarbonate excretion was unchanged between WT and Mdr2−/− mice (NS = not significant), but was reduced in Mdr2−/− mice treated with cromolyn sodium compared to Mdr2−/− mice (B). Total bile acid composition in bile was reduced in Mdr2−/− mice treated with or without cromolyn sodium compared to WT (C), whereas serum bile acids (D) and total liver homogenate bile acids (E) were increased in Mdr2−/− mice compared to WT and treatment with cromolyn sodium decreased both serum and total liver homogenate bile acid levels. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of at least 6 experiments from each animal for bile flow; 6 experiments from each animal for bicarbonate excretion, 4 experiments for bile TBA, 10 experiments for serum TBA and 4 experiments for total liver TBA. *p<0.05 versus WT; #p<0.05 versus Mdr2−/− mice.
