Figure 3.
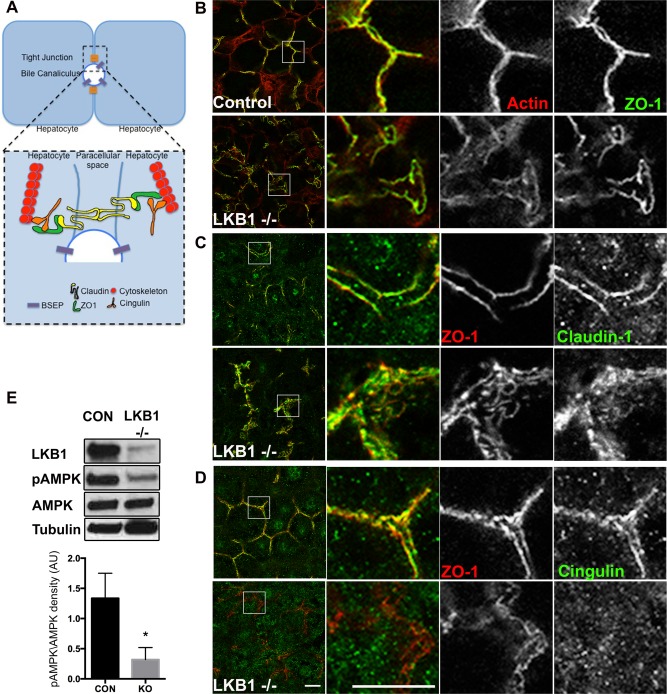
Loss of LKB1 leads to disruption of TJ components and reduced AMPK activation. (A) Simplified schematic representation of TJ organization in hepatocytes. TJs are at the interface of lateral and apical membranes and are composed of transmembrane proteins (claudin; yellow), scaffold proteins (ZO‐1; green), regulatory proteins (cingulin; orange) and cytoskeleton (actin or microtubules; red). (B‐D) Liver sections from control (upper panels) or LKB1−/− (lower panels) were stained with phalloidin, claudin‐1, or cingulin and ZO‐1 antibodies. Note the redistribution of cingulin to the cytosol in LKB1−/− mice compared with control mice. Scale bar: 10 μm. (E) Western blot analysis of LKB1, AMPK, and pAMPK. Total cell lysates of livers from control and LKB1−/− mice were immunoblotted to determine levels of LKB1, AMPK, and phospho‐Thr172 AMPK (pAMPK). Representative western blots are shown. Quantification of pAMPK/AMPK from three independent experiments was plotted as the mean ± SEM (control 1.33 ± 0.23; LKB1−/− 0.31 ± 0.11; P < 0.005).
