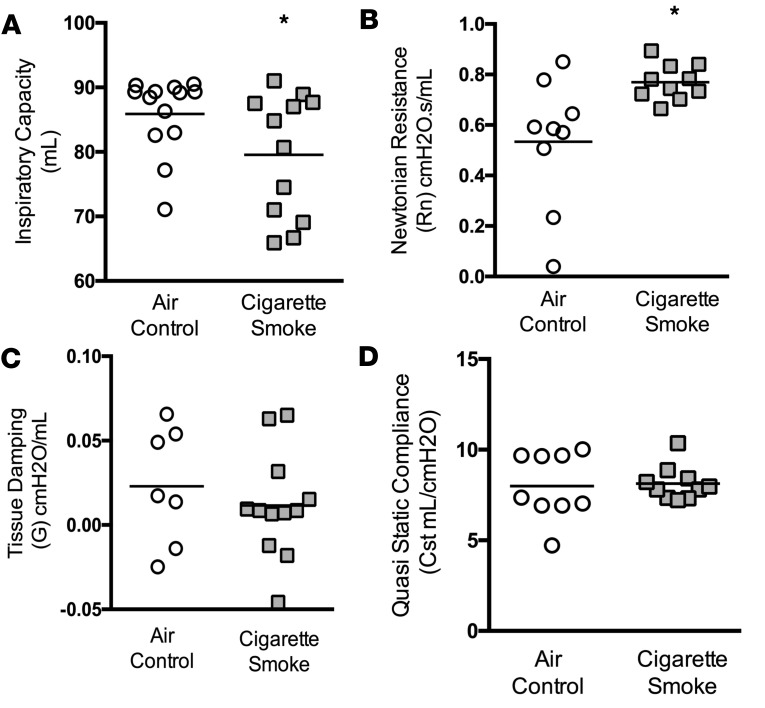
Figure 4. Lung function analyses in a ferret model of COPD.
Functional estimate of airway obstruction in ferrets exposed to cigarette smoke or their corresponding air controls was carried out using a forced oscillometry-based system. (A) Compared with control ferrets, ferrets that underwent chronic smoke exposure for 6 months exhibited significantly diminished inspiratory capacity, a sensitive marker of airway obstruction. (B) Newtonian resistance, a measure of airway resistance of the conducting airways, was elevated in COPD ferrets. (C and D) Tissue damping (C), a measure of tissue elastance, and quasistatic compliance (D) were not significantly affected by smoking. n = 9–12/group. *P < 0.05.