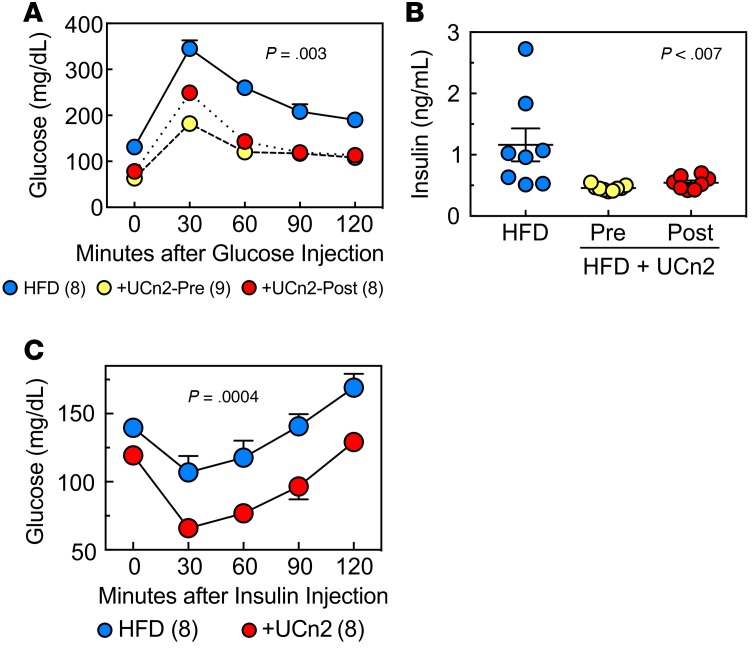
Figure 2. UCn2 gene transfer, glucose disposal, and insulin effectiveness in HFD-fed mice.
(A) Glucose tolerance test 16 weeks after HFD, UCn2 gene transfer before (Pre) vs. at 8 Weeks (Post). Mice received glucose (2 mg/g, i.p.), and glucose was measured sequentially for 120 min. AUC was reduced in mice that had received UCn2 gene transfer, whether it was administered before (+UCn2-Pre; n = 8) or 8 weeks after initiation of HFD (+UCn2-Post; n = 8) (P = 0.003, AUC). The similarity of UCn2-Pre and UCn2-Post glucose levels indicates that UCn2 not only prevented HFD-induced hyperglycemia, but also reduced it once present, indicating a treatment effect. (B) Plasma insulin. UCn2 gene transfer was associated with reduced insulin levels whether given before (Pre) or 8 weeks after (Post) initiation of HFD (P < 0.007; ANOVA). (C) Insulin tolerance test. Nonfasted mice received insulin (0.75 U/kg, i.p.) and blood glucose was assessed. UCn2 gene transfer (given at initiation of HFD) was associated with increased insulin sensitivity (P = 0.0004).