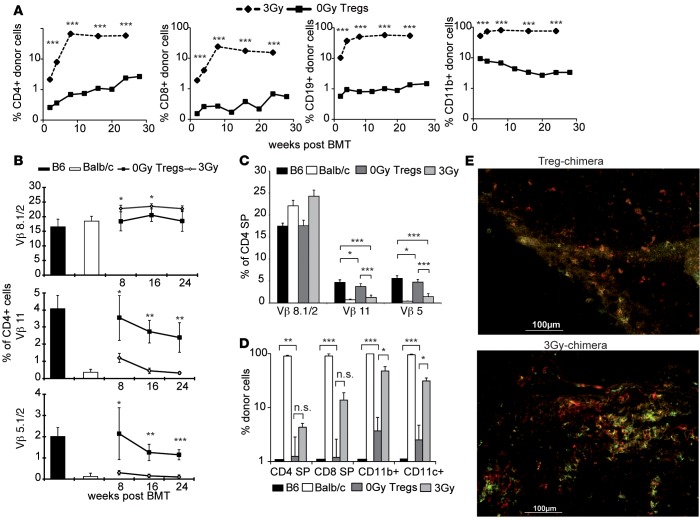
Figure 1. Treg treatment replaces irradiation to induce multilineage chimerism and central tolerance.
Groups of B6 mice were treated with a costimulation blockade–based BMT protocol and grafted with 2 × 107 BALB/c BM cells to induce donor-specific tolerance. BMT recipients were additionally treated with nonmyeloablative (3 Gy, n = 8) irradiation or recipient-derived natural Tregs (nTregs)+ (0-Gy Tregs, n = 6). (A) The majority of recipients in both groups developed permanent multilineage chimerism. Donor (H-2Dd) chimerism among leukocytes of the T cell (CD4+ and CD8+), B cell (CD19+), and myeloid (CD11b/Mac1+) lineage. (B) Deletion of donor-reactive T cells (correlates to Vβ11 and Vβ5 expression) was assessed by flow cytometry of peripheral blood at multiple time points after BMT. (C) Central tolerance was assessed by Vβ expression pattern on intrathymic single-positive (SP) CD4 T cells and (D) the presence of intrathymic chimerism 30 weeks after BMT. Flow cytometric staining verified the engraftment of antigen-presenting donor cells in the thymus and central deletion (30 weeks after BMT). (E) Immunofluorescent staining of frozen thymic sections showed coexpression of CD11c (red) and donor MHC II (I-Ek/d, green). Shown as mean percentage + SD; results are representative of at least 3 independent experiments; ***P < 0.0005, **P < 0.005, *P < 0.05; 2-tailed t test.