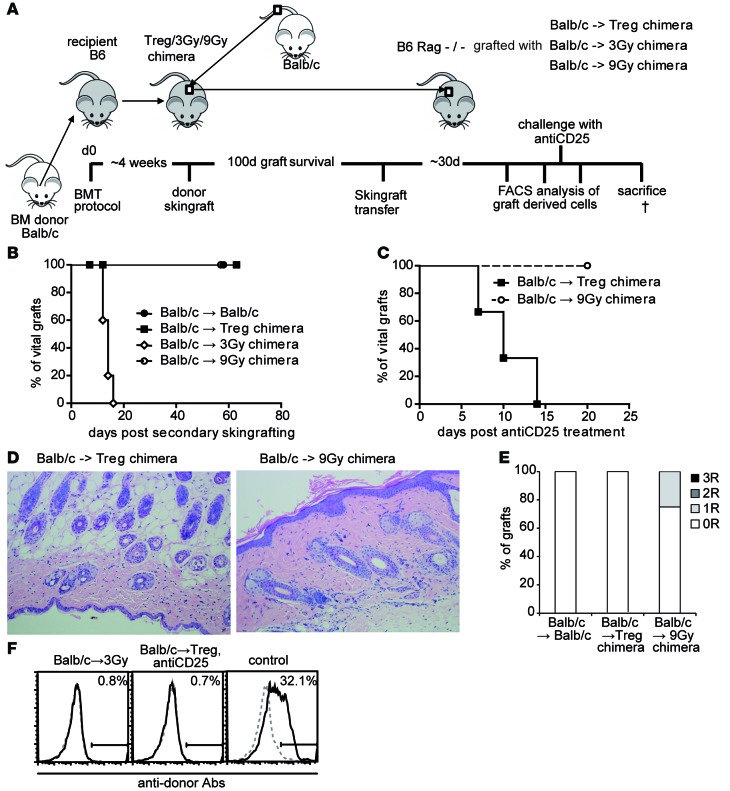
Figure 4. Tolerance in Treg chimeras is maintained by active intragraft regulatory mechanisms.
(A) Schematic illustration of skin transfer experiment setup. (B) Fully mismatched Balb/c allografts from long-term (100 days) tolerant recipients from different treatment protocols are transferred onto RAG–/–-recipient mice. Legend depicts primary donor→recipient combination (BALB/c→BALB/c, n = 3; →Treg chimera, n = 7; →3-Gy chimera, n = 5; →9-Gy chimera, n = 5). (C) Selected RAG–/– recipients with secondary skin grafts are challenged with anti-CD25 (40 days after skin graft transfer; n = 3 each group). (D) Representative histology from transferred skin grafts (>8 weeks postsecondary transfer; H&E staining magnification ×200). (E) Classification of skin allograft pathology (>8 weeks after transfer, n = 3 per group). (F) Reactivity of sera (>8 weeks after skin grafting) with syngeneic (B6; dotted gray) and donor (BALB/c; black) thymocytes shown by flow cytometry through indirect staining with anti–mouse IgG. Representative histograms are shown for RAG skin graft recipients from the groups: 3-Gy chimeras, Treg chimeras after anti-CD25 treatment, and naive control after skin graft rejection. †, time of sacrifice (~d60).