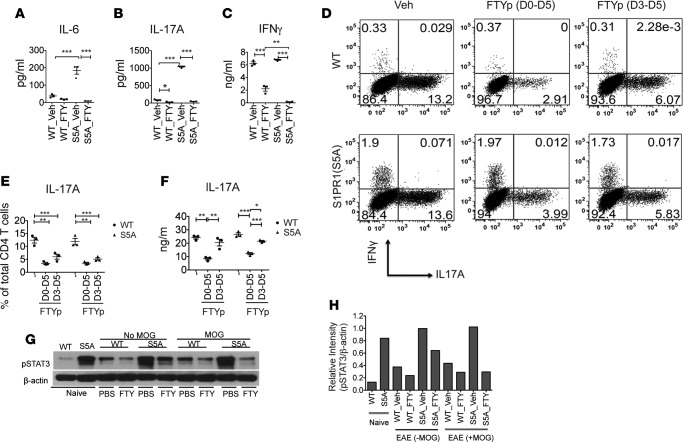
Figure 3. FTY720 treatment downregulated Th17 cell development via targeting STAT3 activation.
Splenocytes from MOG35-55 -immunized C57BL/6J (WT) and S1PR1(S5A) presymptomatic (day 8) EAE mice, treated with FTY720 (0.5 mg/kg, daily i.p injections) or vehicle (1% cyclodextrin in PBS) in vivo, were cultured in the presence of MOG35-55 peptide (10 μg/ml) for 3 days. Culture supernatant was then collected at respective time points (0–72 hours) and analyzed for cytokine expression by ELISA. IL-6 (A) was examined at 24 hours; IL-17A (B) and IFN-γ (C) were examined at 72 hours. CD4+ T cells were isolated from spleens of naive C57BL/6J (WT) and S1PR1(S5A) mice and activated in vitro with anti-CD3 (5 μg/ml) and anti-CD28 (2 μg/ml) for 5 days in Th17 media supplemented with IL-6 (20 ng/ml), IL-23 (20 ng/ml), and TGF-β (1 ng/ml) in the presence of phosphorylated FTY720 (FTYp, 1 μM). Cells were then restimulated with PMA (50 ng/ml) and ionomycin (500 ng/ml) for 4 hours, labeled with antibodies against IFN-γ and IL-17A, and analyzed by flow cytometry (D and E). Culture supernatants were examined by ELISA (F). Splenocytes from MOG35-55-immunized WT and S1PR1(S5A) presymptomatic EAE mice treated in vivo with either FTY720 (0.5 mg/kg) or vehicle by daily i.p. injections were reactivated in vitro with MOG35-55 peptide for 30 minutes. These cells were harvested and lysate was prepared and analyzed by immunoblot analysis utilizing an antibody against pSTAT3 and β-actin (G). Relative protein expression (H) was quantified by densitometric normalization against β-actin expression in the respective samples. Data represent 3 independent experiments (n = 3–5 mice/arm, mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test).