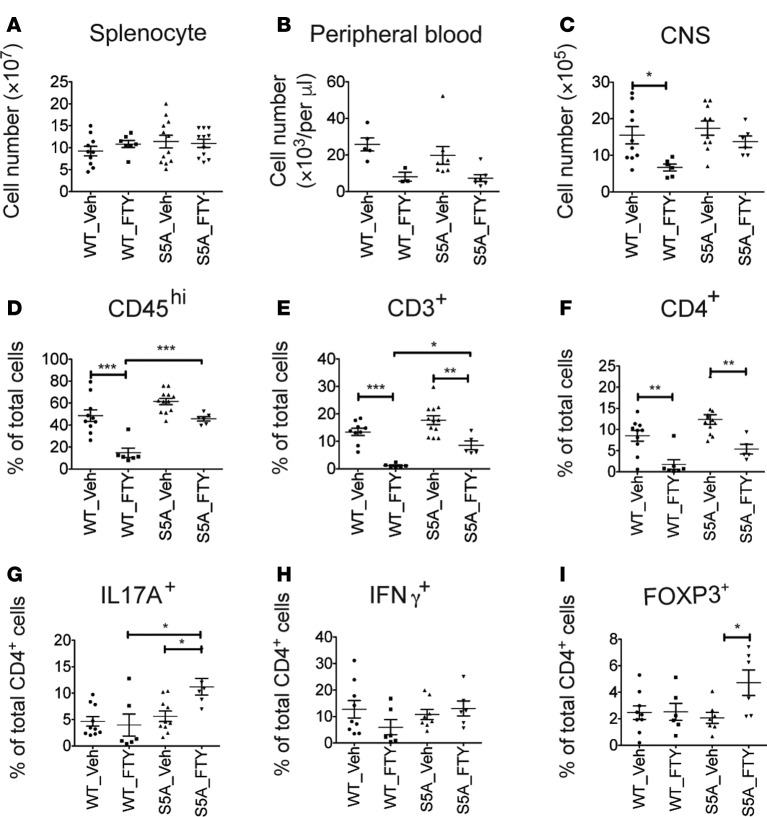
Figure 5. FTY720 treatment failed to arrest immune cell trafficking to the CNS of S1PR1(S5A) EAE mice.
MOG35-55-immunized C57BL/6J (WT) and S1PR1(S5A) EAE mice were treated with vehicle (1% cyclodextrin in PBS) or FTY720 (0.5 mg/kg) by daily i.p. injections. Immune cells from the brains and spinal cords were collected from EAE mice with a score of 2 to 3. Total cell counts from splenocytes (A), peripheral blood mononuclear cells (B), and CNS immune cells (C) were quantified using a hemocytometer. Percentages of CD45hi (D), CD3+ (E), and CD4+ (F) cells among CNS immune cells were quantified by flow cytometry. CNS immune cells were restimulated with PMA (50 ng/ml) and ionomycin (500 ng/ml) for 4 hours, and intracellular staining was performed to measure the expression of IL-17A (G), IFN-γ (H), and FOXP3 (I) among CD4+ cells. This experiment was performed 3 times with n ≥ 5 mice/arm, mean ± SEM, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001, ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test.