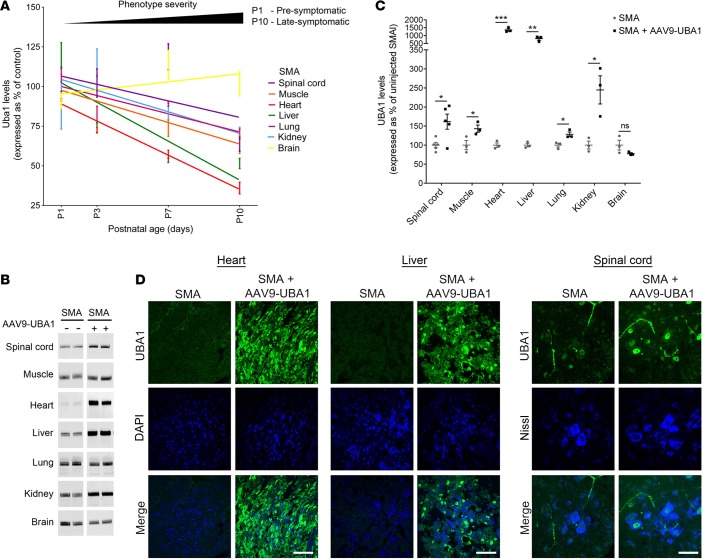
Figure 3. Systemic reductions in Uba1 protein in SMA mice can be restored with AAV9-UBA1 gene therapy.
(A) Quantification of ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (Uba1) levels in the spinal cord, gastrocnemius muscle, heart, liver, lung, kidney, and brain of spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) mice at P1, P3, P7, and P11 by western blot analysis, expressed as a percentage of control values (n = 3 mice for each genotype at each time point). (B and C) Intravenous adeno-associated virus serotype 9–UBA1 (AAV9-UBA1) gene therapy at P1 leads to a significant increase in UBA1 protein levels in the spinal cord, gastrocnemius muscle, heart, liver, lung, and kidney (but not whole brain) in P7 SMA mice, as quantified by Western blot (n = 3 mice per treatment group, except for spinal cord, for which n = 5; unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test). Lanes were run on the same gel but were noncontiguous. (D) Representative confocal micrographs showing increased UBA1 levels (green) in the heart, liver, and motor neurons in the spinal cord ventral horn of P7 AAV9-UBA1–treated mice compared to uninjected SMA mice. Hearts and livers were colabeled with DAPI and the spinal cord fluorescent Nissl stain (blue) (scale bar: 50 μm). ns (not significant) P > 0.05, *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.005.