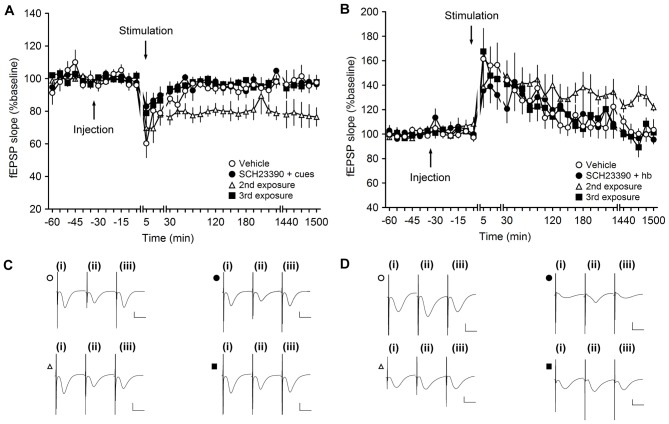
Figure 4.
Antagonism of D1/D5 receptors inhibits learning-facilitated plasticity at MF-CA3 synapses. (A) Weak low-frequency stimulation (wLFS; 1 Hz, 600 pulses) results in short-term depression (STD) in vehicle-treated animals. Upon first exposure to landmark cues, application of wLFS also resulted in STD in animals that were treated with SCH23390 (30 μg). A second exposure (re-exposure) to the same object-place constellations 1 week later resulted in LTD. When the animals explored the cues for a third time (a further week later), wLFS failed to result in LTD. (B) Weak high-frequency stimulation (wHFS, two trains of 100 pulses given at 100 Hz) results in STP in vehicle-treated animals. The first (novel) exposure of the animals to an empty holeboard results in short-term potentiation (STP) in animals that received SCH23390 (30 μg). A second exposure to the same holeboard 1 week later, leads to a facilitation of LTP that lasts for over 24 h. wHFS given during a third exposure to the same holeboard results in STP. Line breaks indicate change in time scale. (C) Analogs represent fEPSP responses obtained in an LTD experiment where a vehicle-treated animal received wLFS only (open circle), and Schaffer collateral (SCH)-treated animal explored the novel cues for the first time (filled circle), an animal that we exposed to the cues for a 2nd time (open triangle) or a 3rd time (filled square). The following time-points are shown: (i) pre-wLFS; (ii) post-wLFS; and (iii) 24 h post-wLFS. (D) Analogs represent fEPSP responses obtained in an LTP experiment where a vehicle-treated animal received wHFS only (open circle), and SCH-treated animal explored the novel cues for the first time (filled circle), an animal that we exposed to the cues for a 2nd time (open triangle) or a 3rd time (filled square). The following time-points are shown: (i) pre-wHFS; (ii) post-wHFS; and (iii) 24 h post-wHFS. Vertical scale bar: 1 mV, horizontal scale bar: 10 ms.