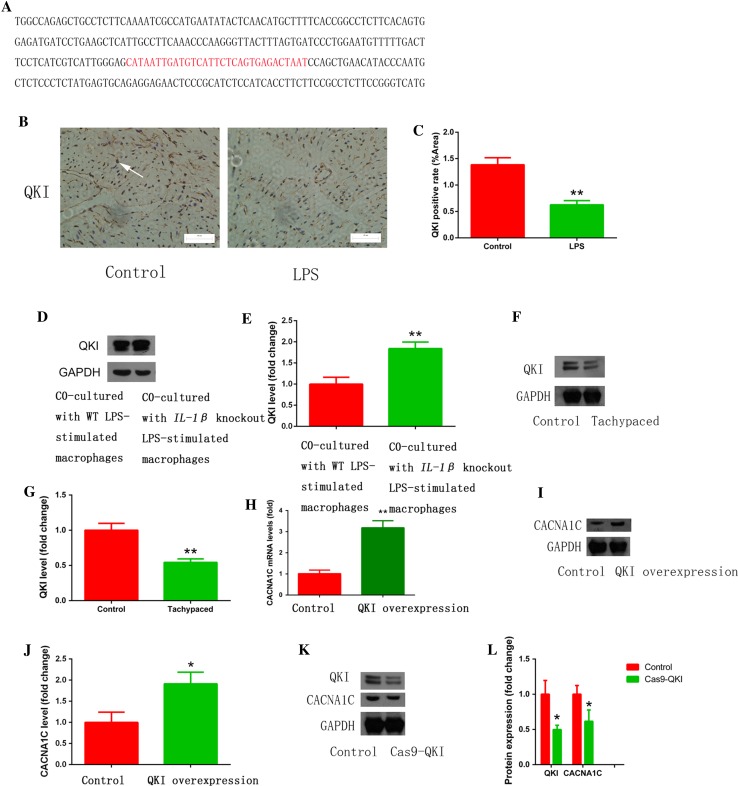
Fig. 5.
Pro-inflammatory macrophages promoted electrical remodeling through regulating QKI expression in atrial myocytes. a The predicted binding sequence (red) of QKI on CACNA1C mRNA. b LPS injection inhibited atrial QKI expression in a mouse model. Immunostaining was performed on atrial myocardium sections using a QKI antibody. Arrow indicates a QKI-positive atrial cardiomyocyte. c The statistical result of b. d Co-culture with IL-1β knockout LPS-stimulated macrophages reversed QKI expression inhibited by LPS-stimulated macrophages. Western blot was used to measure QKI expression in HL-1 cells that were co-cultured with wild type (WT) or IL-1β knockout LPS-stimulated macrophages. GAPDH was used as a loading control. e The statistical result of d. f HL-1 tachypacing inhibited QKI expression. Western blot was used as in d to measure QK1 expression in control or tachypaced HL-1 cells. g The statistical result of f. h, i QKI overexpression increased CACNA1C mRNA and protein expression. RT-qPCR (h) or western blot (i) was performed on RNA or protein lysates obtained from cultured cardiomyocytes with adenoviral-mediated expression of control or QKI. j The statistical result of i. k QKI knockdown decreased CACNA1C expression. l The statistical result of k. Cellular experiments were repeated three times and the sample number of mice in each group was 15. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. control group