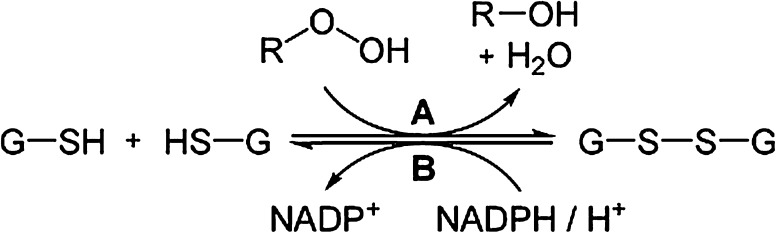
Fig. 3.
Intracellular detoxification by GPx and GSH. Toxic peroxides (R–OOH) are reduced to non-toxic R–OH by the action of the selenoenzymes glutathione peroxidases (A) in the presence of adequate amounts of the co-factor GSH found intracellularly, in contrast to the negligible GSH-levels found extracellularly. GSH is oxidized to its disulphide GSSG in this reaction. The reduced form GSH is regenerated by intracellular glutathione reductase (B) in the presence of NADPH2. This same co-factor, GSH, can also detoxify the compounds glyoxal and methylglyoxal which are neurotoxic byproducts of glucose metabolism, particularly in cases of insulin resistance. The latter reaction requires the presence of the glyoxalase enzyme system (Aaseth et al. 2016)