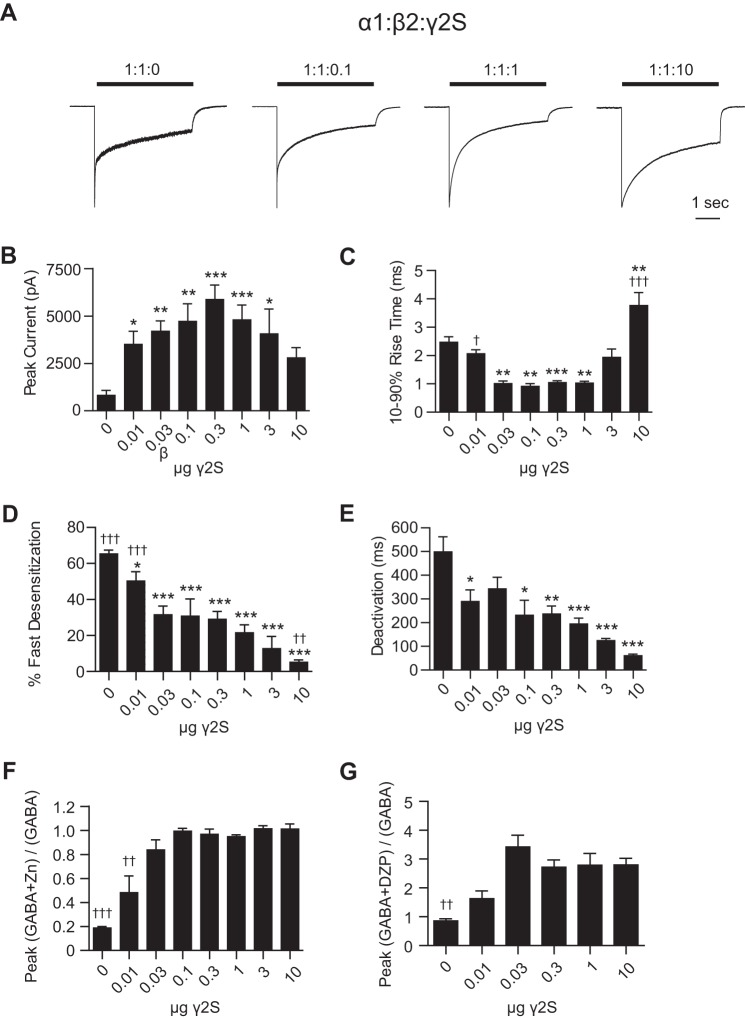
FIGURE 9.
Low levels of γ2 subunit cDNA were sufficient to eliminate kinetic and pharmacological signatures of α1β2 receptors. GABA (1 mm; 4 s) was applied to HEK293T cells transfected with 1 μg of α1, 1 μg of β2, and varying amounts of γ2S subunit cDNA (A). Whole cell currents were recorded and analyzed to determine peak current amplitude (B); 10–90% rise time (C); percent fast desensitization (D) over 4 s from peak amplitude; and weighted time constant of deactivation (E). Representative currents from a subset of transfection conditions are presented in A. F, HEK293T cells transfected with 1 μg of α1, 1 μg of β2, and varying amounts of γ2S subunit cDNA were pretreated (10 s) with Zn2+ (10 μm), and currents were recorded during a 4-s co-application of GABA (1 mm) and Zn2+ (10 μm). Zn2+ resistance was calculated by dividing the peak current amplitude in response to GABA + Zn2+ by the peak current amplitude in response to GABA alone. G, currents were recorded from HEK293T cells transfected with 1 μg of α1, 1 μg of β2, and varying amounts of γ2S subunit cDNA during a 4-s co-application of GABA (∼EC20) and DZP (1 μm). DZP enhancement was expressed as the ratio of peak current amplitude in response to GABA + DZP divided by the peak current amplitude in response to GABA alone. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 versus 1:1:0 and †, p < 0.05; ††, p < 0.01; †††, p < 0.001 versus 1:1:1.