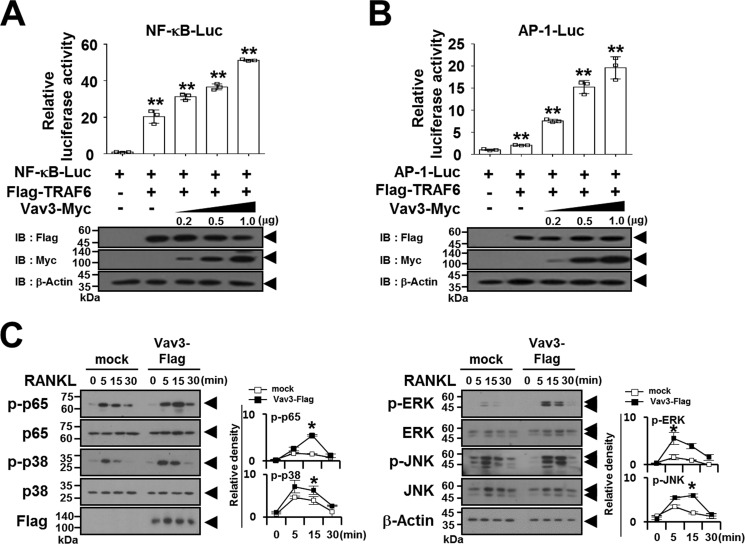
FIGURE 4.
Vav3 expression activates the TRAF6 downstream signaling pathway. A, the effect of Vav3 expression on TRAF6-induced NF-κB activation. 293T cells were transfected with FLAG-TRAF6 (0.15 μg), Vav3-Myc (0.2–1.0 μg), and reporters. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were analyzed using luciferase assays. The cell lysates were normalized for total protein content. The level of Vav3 or TRAF6 expression was detected via anti-Myc (9E10) immunoblotting (IB) or anti-FLAG (M2) IB. β-Actin was used as a loading control. **, p < 0.01. B, the effect of Vav3 expression on TRAF6-induced AP-1 activation. C, the effect of Vav3 expression on RANKL-induced signaling pathways. Puromycin-selected Vav3-expressing BMMs were cultured for 2 h under serum-free conditions. The BMMs were stimulated with RANKL (100 ng/ml) for the indicated times and subsequently analyzed via IB with antibodies that recognized phosphorylated and total NF-κB p65 (Ser536), p38 (Thr180/Tyr182), ERK (Thr202/Thr204), and JNK (Thr183/Tyr185). The cell lysates were normalized for total protein content. The level of Vav3 expression was detected via anti-FLAG IB. The relative level of phosphorylated forms was calculated after normalization to total protein input (right). *, p < 0.05. All experiments were performed at least three times with similar results.