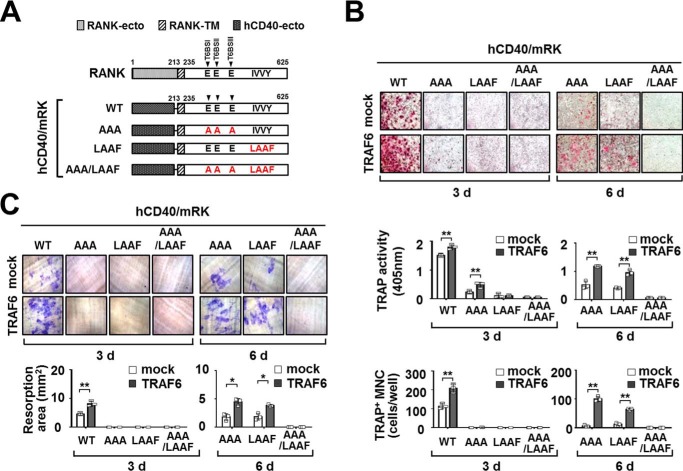
FIGURE 9.
TRAF6 expression enhances osteoclastogenesis through a chimeric hCD40-RANKcyto receptor lacking either T6BSs or the IVVY motif. A, schematic diagram of chimeric hCD40-RANKcyto receptor mutants. The extracellular domain (RANK-ecto) and transmembrane domain (RANK-TM) in RANK are indicated. The numbers shown above each domain diagram denote the amino acid numbers. RANK-ecto of full-length RANK was replaced with the extracellular domain of human CD40 (hCD40-ecto). The Ala mutations of the Glu residues in the T6BS consensus sequences (PXEXX[Ar/Ac]) and the LAAF mutation for the IVVY motif are indicated in RANKcyto. The arrow indicates the position of T6BSs. B, the effect of TRAF6 expression on OC differentiation via a chimeric hCD40-RANKcyto receptor lacking either T6BSs or the IVVY motif. Puromycin-selected BMMs expressing hCD40-RANKcyto with or without TRAF6 were differentiated into OCs with M-CSF (50 ng/ml) and the anti-human CD40 monoclonal antibody G28–5 (100 ng/ml) for 3 or 6 days. The OCs were photographed (top panel, original magnification, ×50) after TRAP staining. The OCs were analyzed using a TRAP solution assay (middle panel). The number of TRAP+ MNCs (at least three nuclei) was counted (bottom panel). mock, empty vector control. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. C, the effect of TRAF6 expression on resorption pit formation via a chimeric hCD40-RANKcyto receptor lacking either T6BSs or the IVVY motif. The resorption pits were visualized (top panel, original magnification, ×50). The summarized data from the resorption pit assays are shown in the bottom panel. All experiments were performed at least three times with similar results.