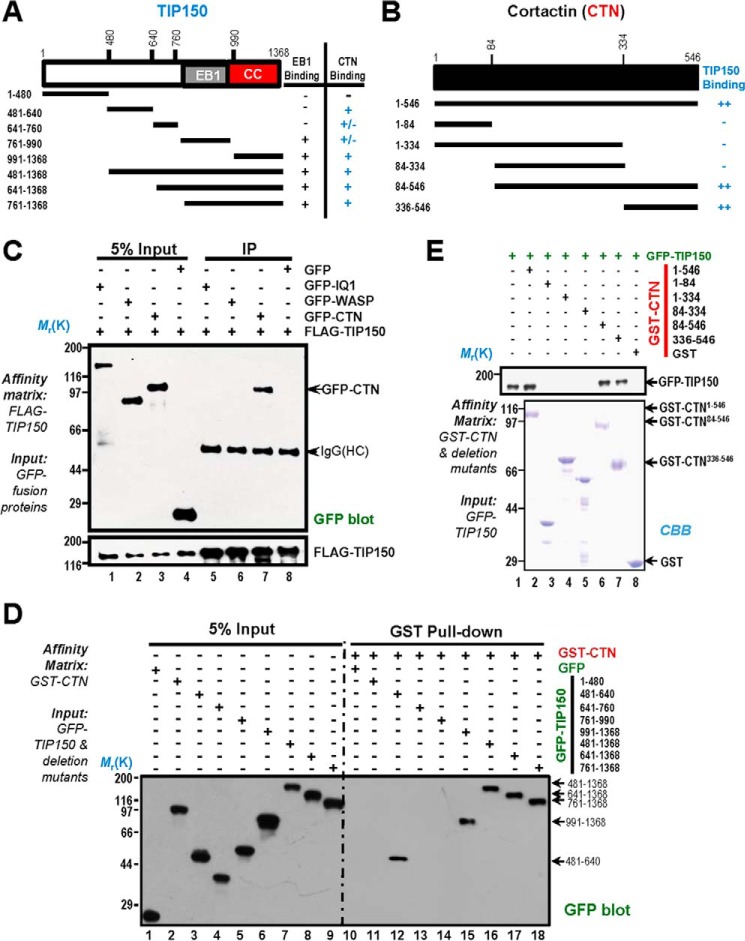
FIGURE 2.
Biochemical characterization reveals a physical link between the TIP150 and CTN. A, schematic of TIP150 truncation mutants. Residue numbers at domain boundaries are indicated. CC, coiled coil. B, schematic of CTN truncation mutants. Residue numbers at domain boundaries are indicated. C, confirmation of the TIP150-CTN interaction. MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with FLAG-TIP150 and GFP-IQGAP, N-WASP, and CTN were lysed and incubated with anti-FLAG M2 affinity matrix. Immunoprecipitates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and detected by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody (top) and anti-FLAG antibody (bottom). IP, immunoprecipitation; HC, heavy chain. D, the TIP150 C terminus binds to the CTN in vitro. Purified GST-CTN fusion proteins were used to isolate GFP-TIP150 deletion mutants from HEK293T cell lysates and fractionated by anti-GFP blotting analysis. E, GST-tagged CTN deletion mutants were purified on glutathione beads and used as an affinity matrix for absorbing a full-length GFP-TIP150 protein from HEK293T cells. GST protein-bound agarose beads were used as a negative control. Anti-TIP150 immunoblotting analyses confirmed that the C-terminal of CTN (amino acids 336–546) is responsible for TIP150-binding (top panel, lane 7). CBB, Coomassie Brilliant Blue.