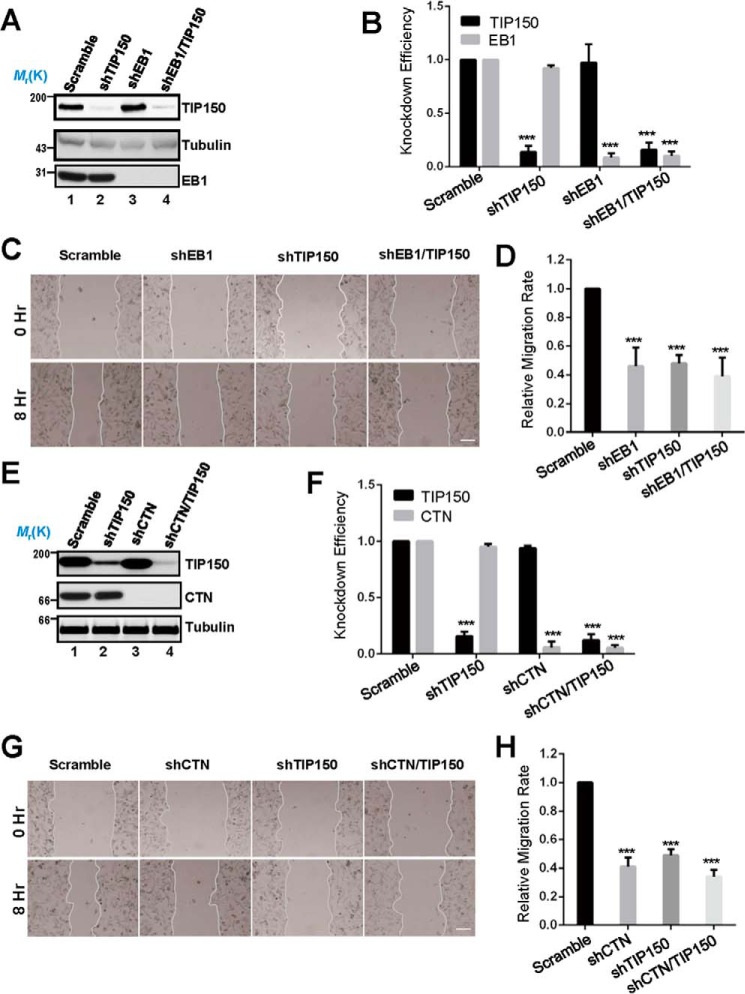
FIGURE 4.
TIP150 and CTN are essential for EGF-elicited cell migration. A, characterization of the knockdown efficiency of TIP150 shRNA and EB1 shRNA. The protein levels of TIP150 and EB1 were significantly decreased in cells transfected with corresponding shRNAs. B, quantitative analysis of the knockdown efficiency of TIP150 shRNA in A. The data represent mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001. C, in MDA-MB-231 cells, suppression of either TIP150 or EB1 perturbed directional migration. The cells were treated with the indicated shRNAs for 72 h and were then scratched, followed by visualization with phase-contrast microscopy at the indicated time points. Scale bar = 100 μm. D, relative migration rates in C were calculated and graphed. Statistical significance was evaluated by Student's t test. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001. E, knockdown efficiency of CTN shRNA. MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with the indicated shRNA for 72 h and then subjected to immunoblotting. TIP150 shRNA was used as a control. F, quantitative analysis of the knockdown efficiency of CTN shRNA in E. Data represent mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001. G, in MDA-MB-231 cells, suppression of CTN or TIP150 caused defects in directional migration. The cells were treated with the indicated shRNAs for 72 h and were then scratched, followed by visualization with phase-contrast microscopy at the indicated time points. Scale bar = 100 μm. H, quantitative analysis of the relative migration velocities of cells toward the opposite side in G. Data are presented as mean ± S.E. from three independent experiments. ***, p < 0.001.