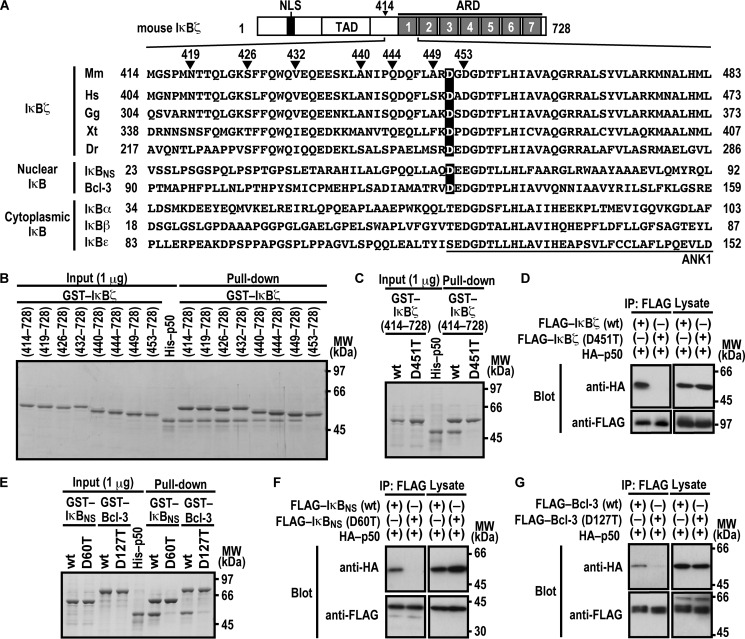
FIGURE 1.
Asp-451 in ANK1 of IκBζ and the corresponding residues of IκBNS and Bcl-3 are involved in interaction with NF-κB p50. A, domain organization of mouse IκBζ and comparison of the amino acid sequences of ANK1 and its N-terminally flanking region. Mouse IκBζ of 728 amino acids contains the nuclear localization signal (NLS), the trans-activation domain (TAD), and the ARD comprised of seven ANK motifs. The amino acid sequences of ANK1 and its N-terminally flanking region of IκBζ from various species and those of other mouse IκB proteins are aligned. Mm, Mus musculus; Hs, Homo sapiens; Gg, Gallus gallus; Xt, Xenopus tropicalis; Dr, Danio rerio. B, the IκBζ N-terminal boundary required for interaction with NF-κB p50. GST-fused IκBζ with the indicated truncation was incubated with His-p50 and pulled down with glutathione-Sepharose-4B beads, followed by SDS-PAGE analysis with CBB staining. MW, molecular weight. C and E, the role for IκBζ Asp-451, IκBNS Asp-60, and Bcl-3 Asp-127 in interaction with NF-κB p50 in vitro. GST-fused IκBζ (C), IκBNS (E), or Bcl-3 (E) with or without the indicated amino acid substitution was incubated with His-p50, followed by analysis as in B. D, F, and G, the role of IκBζ Asp-451, IκBNS Asp-60, and Bcl-3 Asp-127 in interaction with NF-κB p50 in vivo. FLAG-tagged IκBζ (D), IκBNS (F), or Bcl-3 (G) with or without the indicated amino acid substitution was co-expressed with HA-p50 in HEK293T cells, and proteins in the cell lysate were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG antibody, followed by immunoblot analysis with the indicated antibody (Blot). Positions for marker proteins are indicated in kilodaltons.