FIGURE 3.
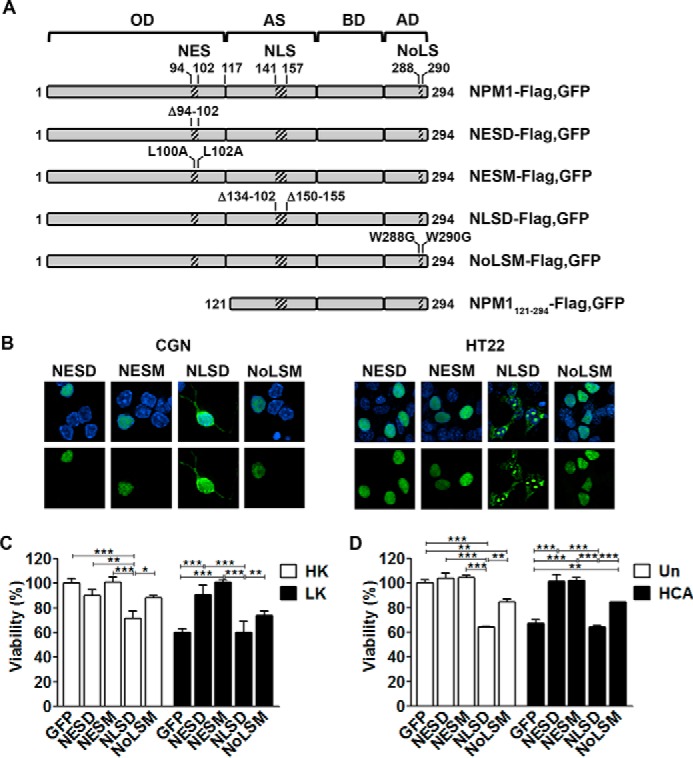
NPM1 toxicity is dependent on subcellular localization. A, schematic detailing the constructs used in this study (adapted from Wang et al. (22)). OD, N-terminal oligomerization domain; AS, acidic stretches; BD, basic domain; AD, aromatic domain. B, representative images showing the localization of NPM1 mutants in CGNs (left panel) and HT22s (right panel). NESD, NESM, NLSD, and NoLSM mutants were transfected into CGNs for 24 h, followed by 24-h HK treatment, or HT22s for 24 h. The cells were then fixed and DAPI-stained, and NPM1 localization was imaged by EGFP autofluorescence. C, CGNs transfected with EGFP, NESD, NESM, NLSD, or NoLSM and treated with HK/LK medium. Viability was quantified by immunocytochemistry with GFP or FLAG antibodies and DAPI staining. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 (n = 3). D, cortical neurons transfected with EGFP and the four NPM1 mutants for 8 h followed by HCA treatment for 15–16 h. Viability was quantified as just described. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 (n = 3).
