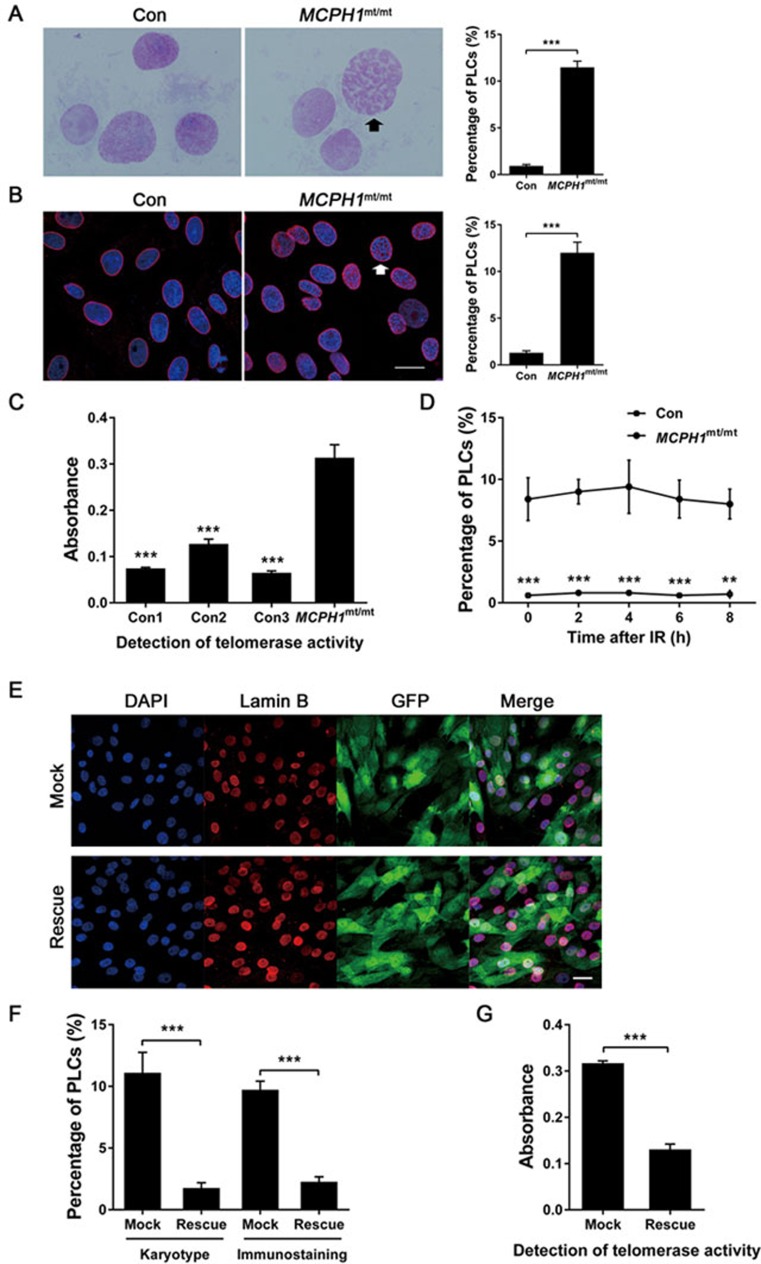
Figure 4.
Cellular phenotype of TALEN-targeted MCPH1 gene mutant monkey. (A) Chromosome preparations of normal and MCPH1mt/mt DFs without prior colchicine treatment. A high proportion of prophase-like cells (black arrow) are present in the MCPH1mt/mt DFs. The histogram depicts the proportion of cells with a prophase-like appearance. (B) Immunofluorescence analysis of lamin B (red) and DAPI (blue) in normal and MCPH1mt/mt DFs. Many of the MCPH1mt/mt DFs exhibit intact nuclear membranes with prematurely condensed chromosomes. A cell (white arrow) shows a remarkable prophase-like appearance. The histogram shows the proportion of cells with a prophase-like appearance. Bar = 20 μm. (C) Telomerase enzymatic activity in DFs was assessed using the telomeric repeat amplification protocol (TRAP) versus MCPH1mt/mt monkey (one-way ANOVA). (D) The proportion of cells with a prophase-like appearance in MCPH1mt/mt DFs after ionizing irradiation. (E) Immunofluorescence analysis of lamin B (red) and DAPI (blue) in MCPH1mt/mt DFs. GFP fluorescence reflects the viral infection efficiency. Bar = 20 μm. (F) The histogram depicts the proportion of cells with a prophase-like appearance among MCPH1mt/mt DFs transfected with vectors encoding eGFP (Mock) or MCPH1-eGFP (Rescue). “Karyotype” indicates the chromosome preparation experiment, whereas “immunostaining” indicates the immunofluorescence analysis of lamin B. (G) Telomerase enzymatic activity was quantified by TRAP in MCPH1mt/mt DFs transfected with vectors encoding eGFP (Mock) or MCPH1-eGFP (Rescue). All data are represented as the mean ± SEM, n = 3, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student's t-test expect C). Con, wild-type monkey; MCPH1mt/mt, MCPH1 mutant monkey; Mock, eGFP expression vector; Rescue, MCPH1-eGFP expression vector; PLCs, prophase-like cells.