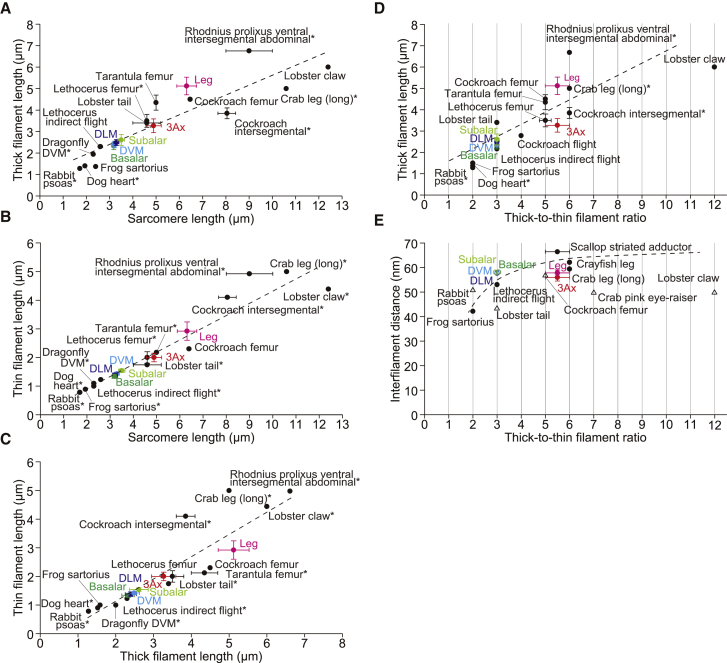
Figure 4.
Correlations among the filament length, sarcomere length, thick/thin filament ratio, and interfilament distance. (A–E) Correlations between the lengths of sarcomeres and the thick filaments (A), between the lengths of sarcomeres and thin filaments (B), between the lengths of thick and thin filaments (C), between the thick/thin filament ratio and the thick-filament length (D), and between the thick/thin filament ratio and the interfilament distance of the thick filaments (E). The plots include the values determined in this study (color coded) and in previous studies (black). Solid circles, x-ray diffraction recordings from intact muscles; open circles, x-ray diffraction recordings from glycerinated muscles; open triangles, electron microscopy. For some data (∗), we estimated the values based on the images provided in each reference. Error bars show standard deviations determined in this study or the range of parameters described in references. In (E), error bars for DVM, DLM, basalar, and subalar muscles are not shown because they overlap with the plots. Broken lines show the linear fit: y = 0.45x + 1.09, R2 = 0.79 in (A); y = 0.44x + 0.01, R2 = 0.92 in (B); y = 0.79x + 0.42, R2 = 0.76 in (C); and y = 0.52x + 1.08, R2 = 0.66 in (D). In (E), a broken-line curve is drawn to guide the eye. See Tables S1, S3, and S4 for exact values.