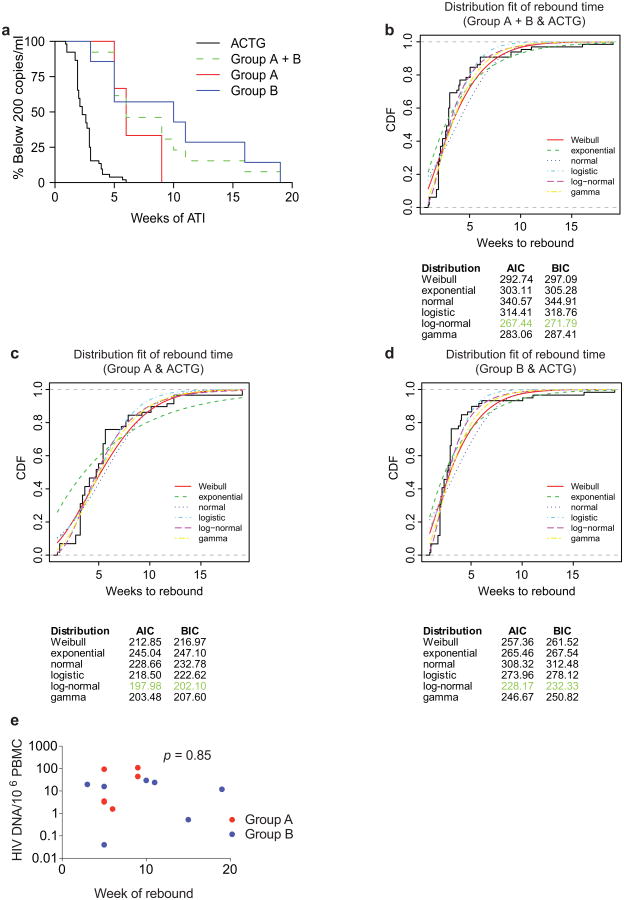
Extended Data Figure 4. Viral rebound in ACTG control subjects and trial participants.
a, Kaplan–Meier plot summarizing viral rebound in 52 ACTG trial participants who underwent ATI without antibody treatment (black, Supplementary Table 6) and trial participants (Fig. 2a, b, Supplementary Table 4). Six group A participants are shown in red, seven Group B participants in blue and the combination in green as indicated. The y-axis indicates the percentage of participants with viral levels below 200 RNA copies per ml, x-axis indicates weeks after ATI initiation. The survival curves of all considered partitions of the trial participants (group A, group B and group A + B) differed significantly at significance level α = 0.05 from the survival curve of the ACTG trial participants. For the comparison of group A (group A + B) with the ACTG trial participants, we performed a weighted log-rank test adjusting for the clinical variables ‘years on ART’ and ‘age’ to correct for possible confounding factors (Supplementary Table 7 P <0.00001). We identified those potential confounders by univariate parametric survival regression using a likelihood ratio test (Statistical Methods). Since we did not discover any confounders with the same analysis among all available clinical variables for the comparison between group B participants and the ACTG trial participants, we performed a standard log-rank test in that setting (P < 0.0001). b–d, In order to perform a survival regression, the distribution of the rebound times has to be determined. Therefore, we compared the empirical cumulative distribution function (CDF) of the rebound times (black, solid line) with the CDF of the rebound times to a fitted distribution (Weibull, exponential, normal, logistic, log-normal, and gamma) for each comparison group (combined trial participants, group A or group B with ACTG control patients). Since the Akaike information criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) were smallest for the log-normal distribution (green), we have chosen to model the rebound times with the log-normal distribution. e, Dot plot indicating the relationship between cell associated HIV DNA in pre-infusion PBMCs (y-axis) and the week of rebound (x-axis). Group A and group B participants are coloured red and blue respectively. The P value was derived from calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient.