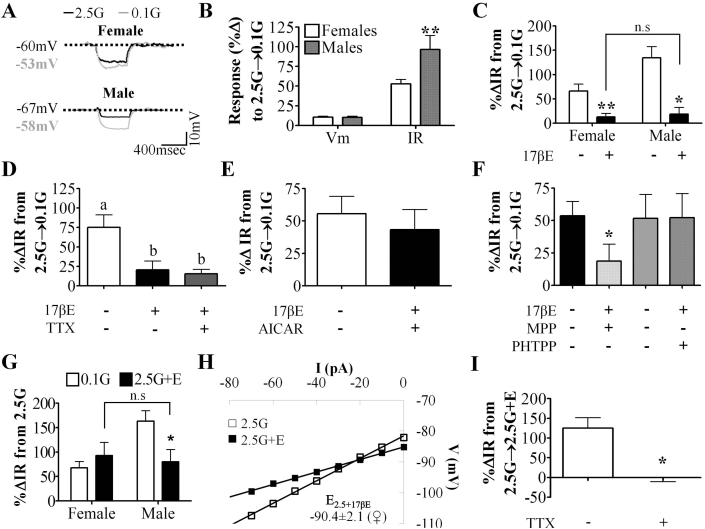
Figure 2.
VL-VMN nonadapting GI neurons are inherently sexually dimorphic and 17βE sensitive. (A) Representative voltage responses to a hyperpolarizing pulse for nonadapting GI neurons from both sexes. Vm was normalized to 2.5 mM glucose to emphasize changes in IR. (B) Quantification of %ΔVm and %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM (♀n = 48, ♂n = 18) glucose in nonadapting GI neurons from both sexes. (C) Quantification of %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose in the presence and absence of 17βE (100 nM) for nonadapting GI neurons from females (n = 9) and males (n = 6). n.s: not significant via unpaired students t-test. (D) Quantification of %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose in the presence and absence of TTX (n = 5) and 17βE (n = 5). Columns with different letters are significantly different from each other as determined by repeated measures one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post-hoc tests. (E, F) Quantification of %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose in the presence and absence 17βE and AICAR, (E, n = 4), MPP (F, n = 5) or PHTPP (F, n = 6). *p < 0.05 via unpaired students t-test. (G) Quantification of %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose and 2.5 mM glucose+17βE in nonadapting GI neurons from females (n = 12) and males (n = 5). n.s: not significant via unpaired students t-test; p < 0.05 via paired students t-test. (H) Representative 17βE-sensitive V-I relationship in 2.5 mM glucose in female nonadapting GI neurons (n = 9). The 17βE-sensitive conductance in 2.5 mM glucose reversed near the K+ equilibrium potential (EK+ = −99 mV) for our solutions. (I) Quantification of %ΔIR in response to 2.5G+17βE (n = 4) in the presence and absence of TTX. *p < 0.05 via paired students t-test. 17βE:17β-Estradiol (100 nM), AICAR: AMPK agonist (0.5 mM), G: mM glucose, IR: input resistance, MPP: ERα antagonist (10 μM), PHTPP: ERβ antagonist (1 μM), TTX: tetrodotoxin (voltage-gated Na+ channel blocker; 500 nM), Vm: membrane potential.