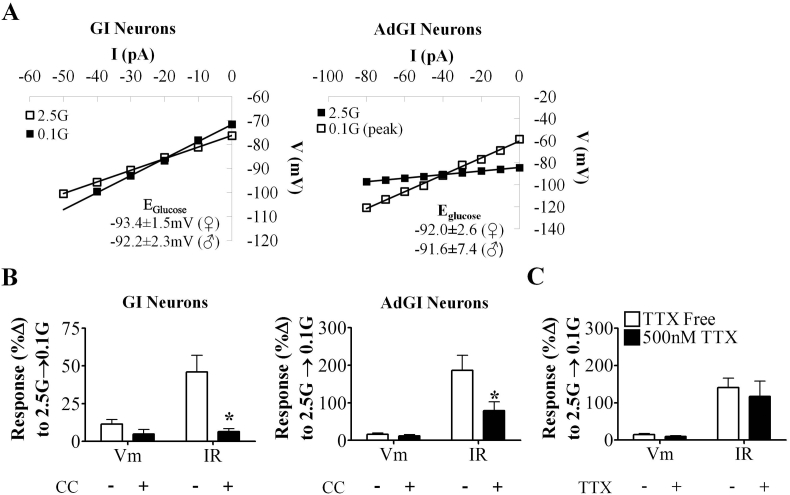
Figure 5.
VL-VMN nonadapting GI neurons and AdGI utilize an AMPK-dependent glucose sensing mechanism. (A) Representative glucose-sensitive V-I relationship in nonadapting GI neurons (left; ♀n = 13, ♂n = 7) and AdGI neurons (right; ♀n = 6, ♂n = 3). The glucose-sensitive conductance reversed near the K+ (EK+ = −99 mV) equilibrium potential for our solutions. (B) Quantification of %ΔVm and %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose in the presence and absence of CC in female nonadapting GI neurons (left; n = 6) and female AdGI neurons (right; n = 6). (C) Quantification of %ΔVm and %ΔIR in response to 0.1 mM glucose in of female AdGI neurons in the presence and absence of TTX (n = 7) *p < 0.05 via paired student t-test. AMPK: AMP-activated kinase, CC: Compound C (AMPK antagonist; 10 μM), G: mM glucose, IR: input resistance, TTX: tetrodotoxin (voltage-gated Na+ channel antagonist; 500 nM), Vm: membrane potential.