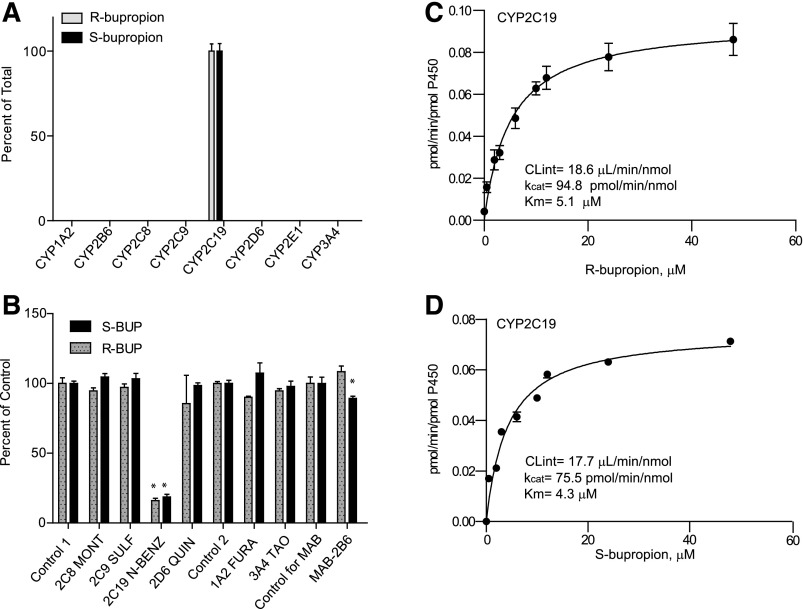
Fig. 3.
Stereoselective metabolism of S- and R-bupropion to 4′-OH-bupropion by recombinant P450 enzymes and human liver microsomes. (A) 4′-OH-bupropion formation from R- and S-bupropion (1 µM) in a panel of P450 supersomes. (B) Inhibition of 4′-OH-bupropion formation from R- and S-bupropion (1 µM) in HLM as percentage of control following incubation of R- or S-bupropion in the presence of selective P450 inhibitors or a CY2B6 inhibitory antibody (MAB-2B6). Control 1 is the control for the reversible inhibitors montelukast (2C8 MONT), sulfaphenazole (2C9 SULF), (+)-N-3-benzylnirvanol (2C19 N-BENZ), and quinidine (2D6 QUIN). Control 2 is the control for time-dependent inhibitors troleandomycin (3A4 TAO) and furafylline (1A2 FURA). *p < 0.05 in comparison to control, one-way analysis of variance. (C and D) Formation kinetics of 4′-OH-bupropion from R-bupropion (C) and S-bupropion (D) in CYP2C19 supersomes.