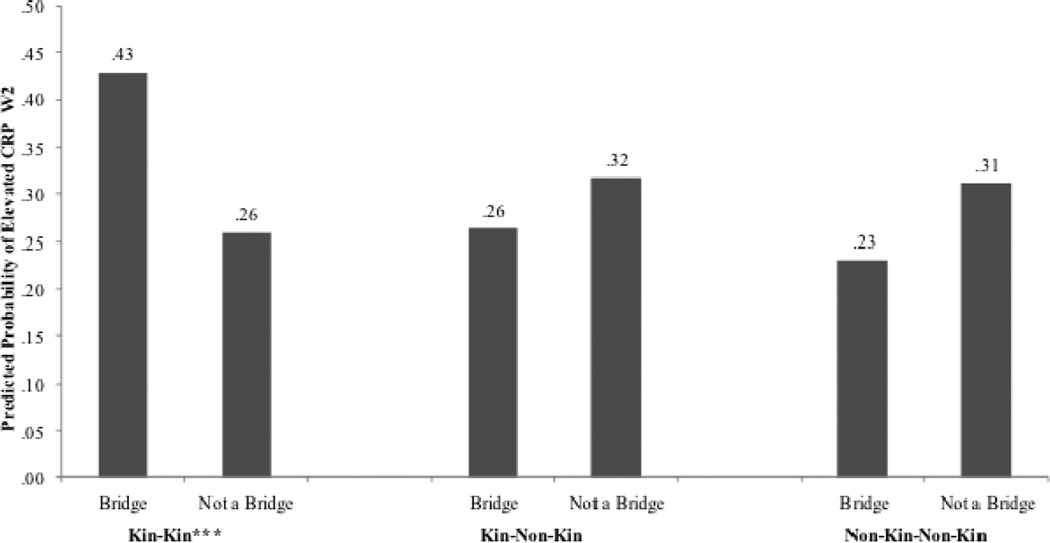
Figure 3.
Marginal Effects of Bridging Status by Type of Alter Pair.
*** p<0.001, ** p<0.01, * p<0.05 (Two-tailed tests).
Note: For each type of alter pair (i.e., kin and kin, kin and non-kin, non-kin and non-kin), marginal effects reflect predicted probabilities of elevated CRP using three separate models (one model for each type of alter pair). Each model is weighted using NSHAP Wave 1 respondent level weights (adjusted for attrition and selection at Wave 2, age, and urbanicity), and is adjusted for multistage, clustered survey design. All covariates (Table 3, Model 4) are held at the mean values for all respondents with at least two network members (regardless of whether they are kin or non-kin), and who provide information on all other variables in the model. Categorical variables are held at their modal values.