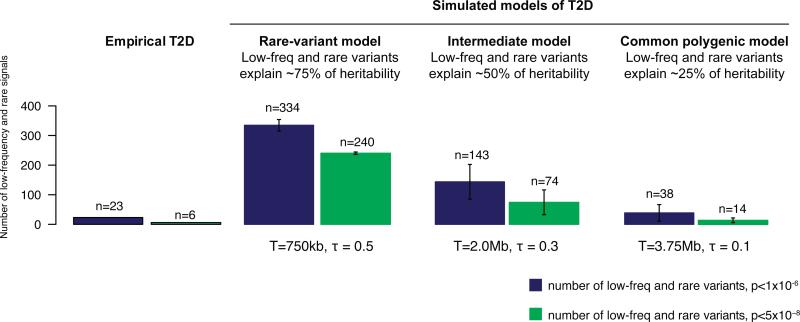
Figure 3. Empirical T2D association results compared to results under different simulated disease models.
Observed number of rare and low-frequency (MAF<5%) genetic association signals for T2D detected genome-wide after imputation compared to the numbers seen under three simulated disease models for T2D which were plausible given results (T2D recurrence risks, GWAS, linkage) prior to large-scale sequencing. Simulated models were defined by two parameters: disease target size T and degree of coupling τ between the causal effects of variants and the selective pressure against them40. Simulated data were generated to match GoT2D imputation quality as a function of MAF (Methods).