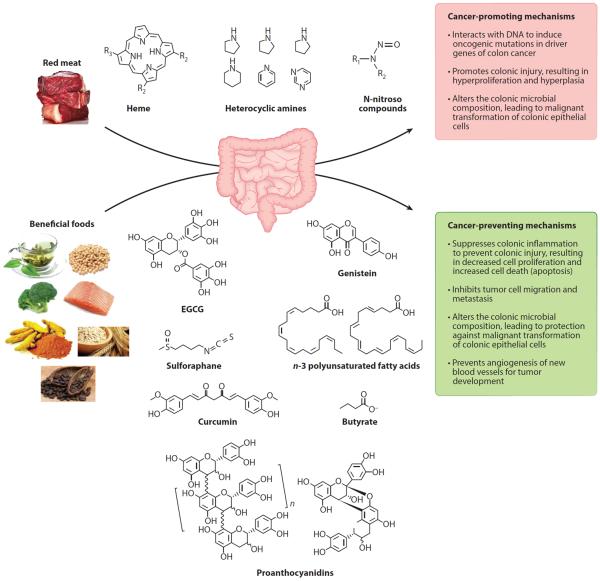
Figure 1.
Effects of diet on promoting and preventing colorectal cancer. Compounds found in the diet have been linked to the development of colorectal cancer through the induction of DNA adducts, leading to mutations in oncogenic genes and promoting hyperproliferation and hyperplasia. Compounds found in many fruits, vegetables, and fish can counteract cancer-promoting compounds in a pleiotropic manner and therefore should be incorporated in a healthy human diet. Abbreviation: EGCG, epigallocatechin gallate.