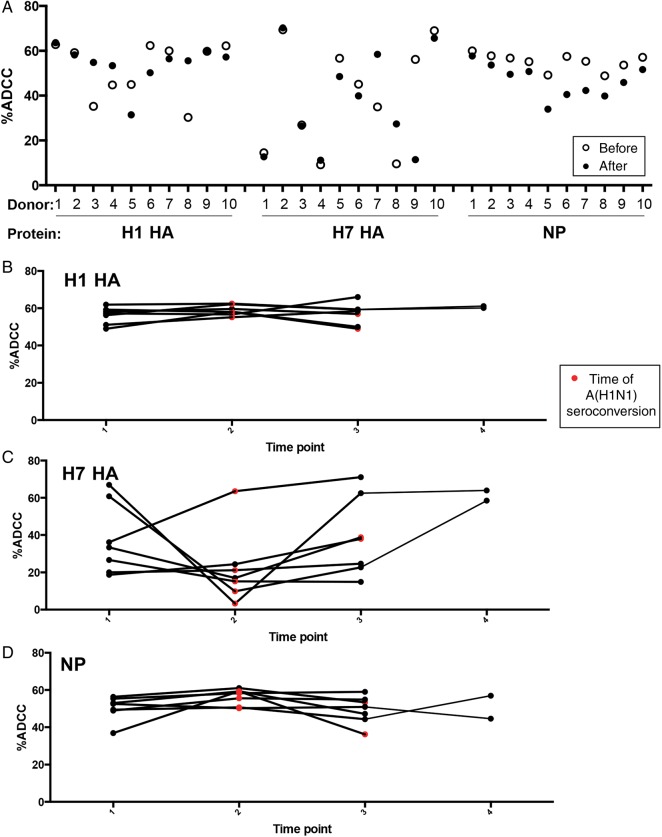
Figure 2.
Longitudinal stability of anti-influenza virus antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) responses is protein specific. A, Paired sera from the same donor (n = 10) before and after influenza A(H1N1)pdm virus exposure (confirmed A[H1N1]pdm positivity was defined as a microneutralization [MN] titer of > 1:40 and a hemagglutination inhibition titer of > 1:40) was assessed for ADCC toward H1 hemagglutinin (HA), H7 HA, and nucleoprotein (NP). Serial longitudinal serum of donors positive for A(H1N1)pdm09 by MN assay (before and after A[H1N1]pdm seroconversion) from 3 (n = 5) and 4 time points (n = 2) were tested for the magnitude of the ADCC response to H1 HA (B), H7 HA (C), and NP (D). The amount of ADCC is the summed total of CD107a+ and/or interferon γ+ cells. Individual responses are given. Red symbols indicate the point of A(H1N1)pdm09 seroconversion, based on MN findings. Time points are intervals between Red Cross blood donations, which are 2–6 months (median, 4 months).