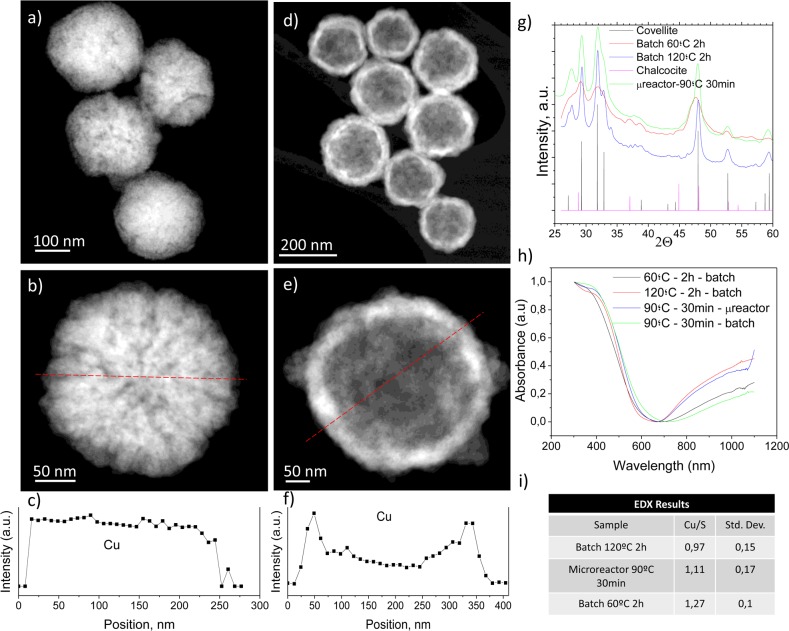
Figure 1.
Physico-chemical characterization of the CuS NPs synthesized in the batch reactor after 2 h of synthesis. STEM-HAADF photographs of the resulting nanoparticles (60 °C, 2 h): (a) sacrificial Cu2O nanoparticles; (b) detail image of a Cu2O nanoparticle. (c) Cu EDS profile of the particle in b. Red dashed line depicts the location of the EDS profile. (d) CuS nanoparticles produced by Kirkendall diffusion. (e) Detailed image of a hollow CuS nanoparticle. (f) Cu EDS profile of the particle in e. Red dashed line in e depicts the location of the EDS profile. (g) X-ray diffractograms of the materials obtained at different temperatures (60 and 120 °C) and the characteristic covellite and chalcocite Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS) patterns; (h) UV–vis absorption spectra of the materials synthesized in both batch and microfluidic reactors. (i) Cu/S atomic ratio of produced nanoparticles. Statistics were conducted after analyzing 20 nanoparticles.