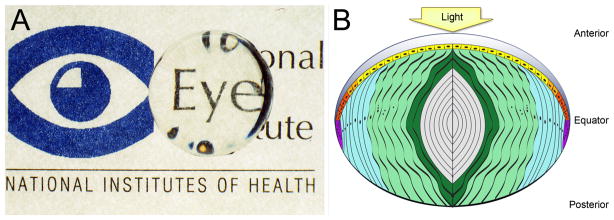
Figure 1.
A) A cow lens placed over the National Eye Institute logo showing both the clarity and refractive properties of the ocular lens. B) Parts of the lens. The lens is composed of two cell types: a monolayer of epithelial cells seen on the anterior surface, which proliferate and differentiate to fiber cells which make up the majority of the lens. Light yellow– light; dark grey– lens capsule; yellow– central epithelium; orange– germinative zone; red– transition zone; purple– meridional row region/bow region; light blue– outer cortical fiber cells; light green-inner cortical fiber cells; dark green– beginning nuclear fiber cells; light gray– nuclear fiber cells including the primary fiber cells which are found at the very center.